Essential role of JunD in cell proliferation is mediated via MYC signaling in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 30763715
- PMCID: PMC6414252
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.02.005
Essential role of JunD in cell proliferation is mediated via MYC signaling in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
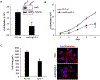
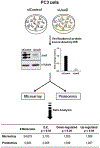
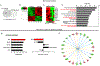
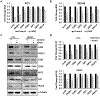
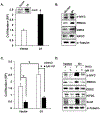
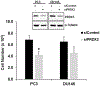
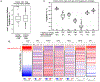
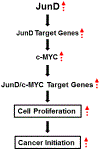
JunD, a member of the AP-1 family, is essential for cell proliferation in prostate cancer (PCa) cells. We recently demonstrated that JunD knock-down (KD) in PCa cells results in cell cycle arrest in G1-phase concomitant with a decrease in cyclin D1, Ki67, and c-MYC, but an increase in p21 levels. Furthermore, the over-expression of JunD significantly increased proliferation suggesting JunD regulation of genes required for cell cycle progression. Here, employing gene expression profiling, quantitative proteomics, and validation approaches, we demonstrate that JunD KD is associated with distinct gene and protein expression patterns. Comparative integrative analysis by Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) identified 1) cell cycle control/regulation as the top canonical pathway whose members exhibited a significant decrease in their expression following JunD KD including PRDX3, PEA15, KIF2C, and CDK2, and 2) JunD dependent genes are associated with cell proliferation, with MYC as the critical downstream regulator. Conversely, JunD over-expression induced the expression of the above genes including c-MYC. We conclude that JunD is a crucial regulator of cell cycle progression and inhibiting its target genes may be an effective approach to block prostate carcinogenesis.
Keywords: Cancer initiation; Cell cycle regulation; JunD; Prostate cancer; c-MYC.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
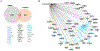
Similar articles
-
JunD Is Required for Proliferation of Prostate Cancer Cells and Plays a Role in Transforming Growth Factor-β (TGF-β)-induced Inhibition of Cell Proliferation.J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 19;291(34):17964-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.714899. Epub 2016 Jun 29. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27358408 Free PMC article.
-
MEN1 silencing aggravates tumorigenic potential of AR-independent prostate cancer cells through nuclear translocation and activation of JunD and β-catenin.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Aug 26;40(1):270. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02058-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34446068 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive activation of nuclear factor kappaB p50/p65 and Fra-1 and JunD is essential for deregulated interleukin 6 expression in prostate cancer.Cancer Res. 2003 May 1;63(9):2206-15. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12727841
-
Regulation of cell cycle entry and G1 progression by CSF-1.Mol Reprod Dev. 1997 Jan;46(1):11-8. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2795(199701)46:1<11::AID-MRD3>3.0.CO;2-U. Mol Reprod Dev. 1997. PMID: 8981358 Review.
-
Myc and the cell cycle.Front Biosci. 1998 Feb 15;3:d250-68. doi: 10.2741/a239. Front Biosci. 1998. PMID: 9468463 Review.
Cited by
-
Down regulated oncogene KIF2C inhibits growth, invasion, and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through the Ras/MAPK signaling pathway and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Feb;10(3):151. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-6240. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35284538 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a tumor immune cell infiltration-related gene signature for recurrence prediction by weighted gene co-expression network analysis in prostate cancer.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 16;14:1067172. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1067172. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37007952 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-383-5p promotes schistosomiasis-induced liver fibrosis by targeting peroxiredoxin-3.Parasit Vectors. 2025 Jun 3;18(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s13071-025-06824-w. Parasit Vectors. 2025. PMID: 40462224 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic clustering tendency of transcription factors reflects phase-separated transcriptional condensates at super-enhancers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 24;53(3):gkaf015. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf015. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39868536 Free PMC article.
-
PRNCR1: a long non-coding RNA with a pivotal oncogenic role in cancer.Hum Genet. 2022 Jan;141(1):15-29. doi: 10.1007/s00439-021-02396-8. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 34727260 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sonnenburg DW, Morgans AK, Emerging Therapies in Metastatic Prostate Cancer, Current oncology reports, 20 (2018) 46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

