MicroRNA-375 Suppresses the Growth and Invasion of Fibrolamellar Carcinoma
- PMID: 30763770
- PMCID: PMC6468197
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.01.008
MicroRNA-375 Suppresses the Growth and Invasion of Fibrolamellar Carcinoma
Abstract
Background & aims: Fibrolamellar carcinoma (FLC) is a rare liver cancer that primarily affects adolescents and young adults. It is characterized by a heterozygous approximately 400-kb deletion on chromosome 19 that results in a unique fusion between DnaJ heat shock protein family member B1 (DNAJB1) and the alpha catalytic subunit of protein kinase A (PRKACA). The role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in FLC remains unclear. We identified dysregulated miRNAs in FLC and investigated whether dysregulation of 1 key miRNA contributes to FLC pathogenesis.
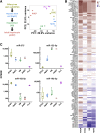
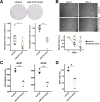
Methods: We analyzed small RNA sequencing (smRNA-seq) data from The Cancer Genome Atlas to identify dysregulated miRNAs in primary FLC tumors and validated the findings in 3 independent FLC cohorts. smRNA-seq also was performed on a FLC patient-derived xenograft model as well as purified cell populations of the liver to determine whether key miRNA changes were tumor cell-intrinsic. We then used clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9) technology and transposon-mediated gene transfer in mice to determine if the presence of DNAJB1-PRKACA is sufficient to suppress miR-375 expression. Finally, we established a new FLC cell line and performed colony formation and scratch wound assays to determine the functional consequences of miR-375 overexpression.
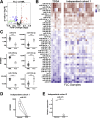
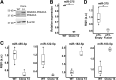
Results: We identified miR-375 as the most dysregulated miRNA in primary FLC tumors (27-fold down-regulation; P = .009). miR-375 expression also was decreased significantly in a FLC patient-derived xenograft model compared to 4 different cell populations of the liver. Introduction of DNAJB1-PRKACA by clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9 engineering and transposon-mediated somatic gene transfer in mice was sufficient to induce significant loss of miR-375 expression (P < .05). Overexpression of miR-375 in FLC cells inhibited Hippo signaling pathway proteins, including yes-associated protein 1 and connective tissue growth factor, and suppressed cell proliferation and migration (P < .05).
Conclusions: We identified miR-375 as the most down-regulated miRNA in FLC tumors and showed that overexpression of miR-375 mitigated tumor cell growth and invasive potential. These findings open a potentially new molecular therapeutic approach. Further studies are necessary to determine how DNAJB1-PRKACA suppresses miR-375 expression and whether miR-375 has additional important targets in this tumor. Transcript profiling: GEO accession numbers: GSE114974 and GSE125602.
Keywords: Cancer Genomics; Fibrolamellar Carcinoma; Pediatric Cancer; miRNA.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Craig J.R., Peters R.L., Edmondson H.A., Omata M. Fibrolamellar carcinoma of the liver: a tumor of adolescents and young adults with distinctive clinico-pathologic features. Cancer. 1980;46:372–379. - PubMed
-
- Stipa F., Yoon S.S., Liau K.H., Fong Y., Jarnagin W.R., D’Angelica M., Abou-Alfa G., Blumgart L.H., DeMatteo R.P. Outcome of patients with fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2006;106:1331–1338. - PubMed
-
- Honeyman J.N., Simon E.P., Robine N., Chiaroni-Clarke R., Darcy D.G., Lim I.I.P., Gleason C.E., Murphy J.M., Rosenberg B.R., Teegan L., Takacs C.N., Botero S., Belote R., Germer S., Emde A.-K., Vacic V., Bhanot U., LaQuaglia M.P., Simon S.M. Detection of a recurrent DNAJB1-PRKACA chimeric transcript in fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma. Science. 2014;343:1010–1014. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cornella H., Alsinet C., Sayols S., Zhang Z., Hao K., Cabellos L., Hoshida Y., Villanueva A., Thung S., Ward S.C., Rodriguez-Carunchio L., Vila-Casadesús M., Imbeaud S., Lachenmayer A., Quaglia A., Nagorney D.M., Minguez B., Carrilho F., Roberts L.R., Waxman S., Mazzaferro V., Schwartz M., Esteller M., Heaton N.D., Zucman-Rossi J., Llovet J.M. Unique genomic profile of fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2014;148:806–818. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

