Pediatric Epilepsy Mechanisms: Expanding the Paradigm of Excitation/Inhibition Imbalance
- PMID: 30764523
- PMCID: PMC6406372
- DOI: 10.3390/children6020023
Pediatric Epilepsy Mechanisms: Expanding the Paradigm of Excitation/Inhibition Imbalance
Abstract
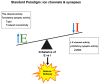
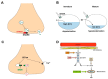
Mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy have traditionally been considered to involve abnormalities of ion channels or synaptic function. Those considerations gave rise to the excitation/inhibition (E/I) imbalance theory, whereby increased excitation, decreased inhibition, or both favor a hyperexcitable state and an increased propensity for seizure generation and epileptogenesis. Several recent findings warrant reconsideration and expansion of the E/I hypothesis: novel genetic mutations have been identified that do not overtly affect E/I balance; neurotransmitters may exert paradoxical effects, especially during development; anti-seizure medications do not necessarily work by decreasing excitation or increasing inhibition; and metabolic factors participate in the regulation of neuronal and network excitability. These novel conceptual and experimental advances mandate expansion of the E/I paradigm, with the expectation that new and exciting therapies will emerge from this broadened understanding of how seizures and epilepsy arise and progress.
Keywords: STXBP1; antiseizure drugs; epilepsy; excitation; genetic mutations; inhibition; ketogenic diet; levetiracetam; metabolism; seizures; synaptic function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stafstrom C.E., Rho J.M. Neurophysiology of seizures and epilepsy. In: Swaiman K.F., Ashwal S., Ferriero D.M., Schor N.F., Finkel R.S., Gropman A.L., Pearl P.L., Shevell M.I., editors. Swaiman’s Pediatric Neurology: Principles and Practice. 6th ed. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2017. pp. 506–512.
-
- Jiruska P., de Curtis M., Jefferys J.G. Modern concepts of focal epileptic networks. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2014;114:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

