Activation of CD8⁺ T Cell Responses after Melanoma Antigen Targeting to CD169⁺ Antigen Presenting Cells in Mice and Humans
- PMID: 30764534
- PMCID: PMC6406251
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11020183
Activation of CD8⁺ T Cell Responses after Melanoma Antigen Targeting to CD169⁺ Antigen Presenting Cells in Mice and Humans
Abstract
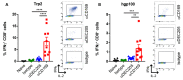
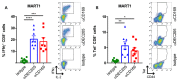
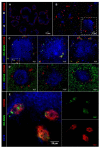
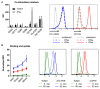
The lack of tumor-reactive T cells is one reason why immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies still fail in a significant proportion of melanoma patients. A vaccination that induces melanoma-specific T cells could potentially enhance the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Here, we describe a vaccination strategy in which melanoma antigens are targeted to mouse and human CD169 and thereby induce strong melanoma antigen-specific T cell responses. CD169 is a sialic acid receptor expressed on a subset of mouse splenic macrophages that captures antigen from the blood and transfers it to dendritic cells (DCs). In human and mouse spleen, we detected CD169⁺ cells at an equivalent location using immunofluorescence microscopy. Immunization with melanoma antigens conjugated to antibodies (Abs) specific for mouse CD169 efficiently induced gp100 and Trp2-specific T cell responses in mice. In HLA-A2.1 transgenic mice targeting of the human MART-1 peptide to CD169 induced strong MART-1-specific HLA-A2.1-restricted T cell responses. Human gp100 peptide conjugated to Abs specific for human CD169 bound to CD169-expressing monocyte-derived DCs (MoDCs) and resulted in activation of gp100-specific T cells. Together, these data indicate that Ab-mediated antigen targeting to CD169 is a potential strategy for the induction of melanoma-specific T cell responses in mice and in humans.
Keywords: CD169; Siglec-1; T cell responses; cancer vaccines; dendritic cell; macrophage; melanoma; sialoadhesin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dobry A.S., Zogg C.K., Hodi F.S., Smith T.R., Ott P.A., Iorgulescu J.B. Management of metastatic melanoma: Improved survival in a national cohort following the approvals of checkpoint blockade immunotherapies and targeted therapies. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018;67:1833–1844. doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-2241-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iorgulescu J.B., Harary M., Zogg C.K., Ligon K.L., Reardon D.A., Hodi F.S., Aizer A.A., Smith T.R. Improved risk-adjusted survival for melanoma brain metastases in the era of checkpoint blockade immunotherapies: Results from a national cohort. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018;6:1039–1045. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0067. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

