Indoxyl Sulfate Induces Apoptosis Through Oxidative Stress and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway Inhibition in Human Astrocytes
- PMID: 30764571
- PMCID: PMC6406290
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8020191
Indoxyl Sulfate Induces Apoptosis Through Oxidative Stress and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway Inhibition in Human Astrocytes
Abstract
Uremic toxins accumulated in chronic kidney disease (CKD) increases the risk of cognitive impairment. Indoxyl sulfate (IS) is a well-known protein-bound uremic toxin that is correlated with several systemic diseases, but no studies on human brain cells are available. We investigated the effect of IS on primary human astrocytes through next-generation sequencing and cell experiment confirmation to explore the mechanism of IS-associated brain damage. Total RNAs extracted from IS-treated and control astrocytes were evaluated by performing functional and pathway enrichment analysis. The toxicities of IS in the astrocytes were investigated in terms of cell viability through flow cytometry; the signal pathway was then investigated through immunoblotting. IS stimulated the release of reactive oxygen species, increased nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 levels, and reduced mitochondrial membrane potential. IS triggered astrocyte apoptosis by inhibiting the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, including extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK), MAPK/ERK kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38. The decreased ERK phosphorylation was mediated by the upregulated dual-specificity phosphatase 1, 5, 8, and 16. In conclusion, IS can induce neurotoxicity in patients with CKD and the pathogenesis involves cell apoptosis through oxidative stress induction and MAPK pathway inhibition in human astrocytes.
Keywords: astrocyte; dual specific phosphatase; indoxyl sulfate; mitogen-activated protein kinase; oxidative stress; uremic toxins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




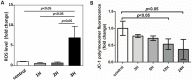
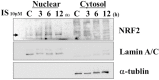


References
-
- O’Lone E., Connors M., Masson P., Wu S., Kelly P.J., Gillespie D., Parker D., Whiteley W., Strippoli G.F., Palmer S.C., et al. Cognition in People with End-Stage Kidney Disease Treated with Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016;67:925–935. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.12.028. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

