Fluorescent DNA Biosensor for Single-Base Mismatch Detection Assisted by Cationic Comb-Type Copolymer
- PMID: 30764576
- PMCID: PMC6384784
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24030575
Fluorescent DNA Biosensor for Single-Base Mismatch Detection Assisted by Cationic Comb-Type Copolymer
Abstract
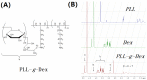
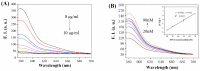
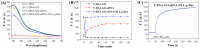
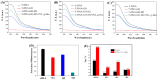
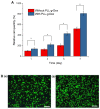
Simple and rapid detection of DNA single base mismatch or point mutation is of great significance for the diagnosis, treatment, and detection of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in genetic diseases. Homogeneous mutation assays with fast hybridization kinetics and amplified discrimination signals facilitate the automatic detection. Herein we report a quick and cost-effective assay for SNP analysis with a fluorescent single-labeled DNA probe. This convenient strategy is based on the efficient quenching effect and the preferential binding of graphene oxide (GO) to ssDNA over dsDNA. Further, a cationic comb-type copolymer (CCC), poly(l-lysine)-graft-dextran (PLL-g-Dex), significantly accelerates DNA hybridization and strand-exchange reaction, amplifying the effective distinction of the kinetic barrier between a perfect matched DNA and a mismatched DNA. Moreover, in vitro experiments indicate that RAW 264.7 cells cultured on PLL-g-Dex exhibits excellent survival and proliferation ability, which makes this mismatch detection strategy highly sensitive and practical.
Keywords: SNP analysis; cationic comb-type copolymer; fluorescent DNA biosensor; graphene oxide; single-base mismatch detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

