8-armed octopus: Evaluation of clinicopathologic prognostic factors of urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary system
- PMID: 30764592
- PMCID: PMC7350879
- DOI: 10.3906/sag-1805-51
8-armed octopus: Evaluation of clinicopathologic prognostic factors of urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary system
Abstract
Background/aim: This study was designed to determine the characteristic features of upper urinary system urothelial carcinomas (UUSUCs) and to evaluate the clinicopathological parameters associated with prognosis.
Materials and methods: A total of 74 cases of UUSUC were included, from three different centers. Demographic data and histopathological features such as tumor localization, concomitant tumor in the urinary system, distant metastasis with overall survival and disease-free survival obtained from the hospital records were evaluated retrospectively. Histopathologic prognostic features such as grade, perineural invasion, lymphovascular invasion, tumor necrosis, and surgical margin status were also evaluated.
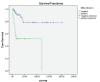
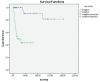
Results: Seventy cases (94.6%) underwent open nephroureterectomy whereas 4 cases (5.4%) had laparoscopic nefroureterectomy. Thirty-eight (51.4%) cases were located in the pelvis, 7 (9.5%) in the ureter, 29 (39.2%) both in the pelvis and ureter. Fifty-six (75.7%) cases were alive; however, 18 (24.3%) patients were found to be dead. pTa, pT1, pT2, pT3, and pT4 tumors were reported in 16 (21.6%), 13 (17.6%), 4 (5.4%), 28 (37.8%), and 13 (17.6%) patients, respectively. Histopathologically, 17 cases (23%) were low-grade, 57 cases (77%) were high-grade. Statistically significant correlation was observed between overall survival and lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, tumor necrosis, and differentiation by univariate analysis. Only distant metastasis was statistically associated with overall survival by multivariate analysis. We found no significant relationship between disease-free survival and all parameters.
Conclusion: Differentiation and necrosis of tumor, lymph node involvement, and presence of distant metastasis is associated with the overall survival of urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary system.
Keywords: Prognostic factors; upper tract urothelial carcinomas; upper urinary tract; urothelial carcinomas.
Conflict of interest statement
none declared
Figures


References
-
- Lughezzani G Burger M Margulis V Prognostic factors in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinomas: a comprehensive review of the current literature. 2012;62:100–114. - PubMed
-
- Miyazaki J Nishiyama H Epidemiology of urothelial carcinoma. Int J Urol. 2017;24:730–734. - PubMed
-
- Leow JJ Martin-Doyle W Fay AP Choueiri TK Chang SL Bellmunt J. A systematic review and metaanalysis of adjuvant and neoadjuvant chemotherapy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2014;66:529–541. - PubMed
-
- Emamekhoo H Dhillon P Gopalakrishnan D Elson P Stephenson A Magi-Galluzzi C McKenney J Harper H Haber GP Kaouk J Prognostic factors and risk stratification in invasive upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018;16:e751–e760. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

