Mechanism of Cross-talk between H2B Ubiquitination and H3 Methylation by Dot1L
- PMID: 30765112
- PMCID: PMC6498860
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.002
Mechanism of Cross-talk between H2B Ubiquitination and H3 Methylation by Dot1L
Abstract
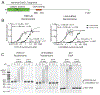
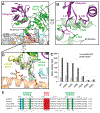
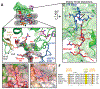
Methylation of histone H3 K79 by Dot1L is a hallmark of actively transcribed genes that depends on monoubiquitination of H2B K120 (H2B-Ub) and is an example of histone modification cross-talk that is conserved from yeast to humans. We report here cryo-EM structures of Dot1L bound to ubiquitinated nucleosome that show how H2B-Ub stimulates Dot1L activity and reveal a role for the histone H4 tail in positioning Dot1L. We find that contacts mediated by Dot1L and the H4 tail induce a conformational change in the globular core of histone H3 that reorients K79 from an inaccessible position, thus enabling this side chain to insert into the active site in a position primed for catalysis. Our study provides a comprehensive mechanism of cross-talk between histone ubiquitination and methylation and reveals structural plasticity in histones that makes it possible for histone-modifying enzymes to access residues within the nucleosome core.
Keywords: Dot1L; chromatin; cryo-EM; histones; methylation; nucleosome; structural biology; ubiquitin.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
C.W. is a member of the scientific advisory board of ThermoFisher Scientific.
Figures

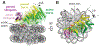


References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, et al. (2010). PHENIX: A comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica Section D: Biological Crystallography 66, 213–221. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

