Five computational developability guidelines for therapeutic antibody profiling
- PMID: 30765520
- PMCID: PMC6410772
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1810576116
Five computational developability guidelines for therapeutic antibody profiling
Abstract
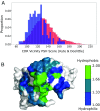
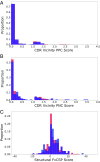
Therapeutic mAbs must not only bind to their target but must also be free from "developability issues" such as poor stability or high levels of aggregation. While small-molecule drug discovery benefits from Lipinski's rule of five to guide the selection of molecules with appropriate biophysical properties, there is currently no in silico analog for antibody design. Here, we model the variable domain structures of a large set of post-phase-I clinical-stage antibody therapeutics (CSTs) and calculate in silico metrics to estimate their typical properties. In each case, we contextualize the CST distribution against a snapshot of the human antibody gene repertoire. We describe guideline values for five metrics thought to be implicated in poor developability: the total length of the complementarity-determining regions (CDRs), the extent and magnitude of surface hydrophobicity, positive charge and negative charge in the CDRs, and asymmetry in the net heavy- and light-chain surface charges. The guideline cutoffs for each property were derived from the values seen in CSTs, and a flagging system is proposed to identify nonconforming candidates. On two mAb drug discovery sets, we were able to selectively highlight sequences with developability issues. We make available the Therapeutic Antibody Profiler (TAP), a computational tool that builds downloadable homology models of variable domain sequences, tests them against our five developability guidelines, and reports potential sequence liabilities and canonical forms. TAP is freely available at opig.stats.ox.ac.uk/webapps/sabdab-sabpred/TAP.php.
Keywords: developability guidelines; immunoglobulin gene sequencing; surface charge; surface hydrophobicity; therapeutic monoclonal antibodies.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: A.P.L. is employed by GlaxoSmithKline plc, B.T. is employed by MedImmune Limited, A.B. is employed by Roche Diagnostics GmbH, and J.S. is employed by UCB Celltech. All four companies discover and sell antibody therapies.
Figures


References
-
- Antibody Society 2018. Approved antibodies. Available at https://www.antibodysociety.org/news/approved-antibodies/. Accessed June 12, 2018.
-
- Jarasch A, et al. Developability assessment during the selection of novel therapeutic antibodies. J Pharm Sci. 2015;104:1885–1898. - PubMed
-
- Xu Y, et al. Addressing polyspecificity of antibodies selected from an in vitro yeast presentation system: A FACS-based, high-throughput selection and analytical tool. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2013;26:663–670. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

