Insulin signaling in the hippocampus and amygdala regulates metabolism and neurobehavior
- PMID: 30765523
- PMCID: PMC6442573
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1817391116
Insulin signaling in the hippocampus and amygdala regulates metabolism and neurobehavior
Abstract
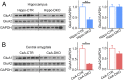
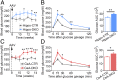
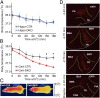
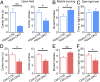
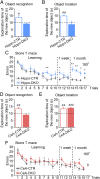
Previous studies have shown that insulin and IGF-1 signaling in the brain, especially the hypothalamus, is important for regulation of systemic metabolism. Here, we develop mice in which we have specifically inactivated both insulin receptors (IRs) and IGF-1 receptors (IGF1Rs) in the hippocampus (Hippo-DKO) or central amygdala (CeA-DKO) by stereotaxic delivery of AAV-Cre into IRlox/lox/IGF1Rlox/lox mice. Consequently, both Hippo-DKO and CeA-DKO mice have decreased levels of the GluA1 subunit of glutamate AMPA receptor and display increased anxiety-like behavior, impaired cognition, and metabolic abnormalities, including glucose intolerance. Hippo-DKO mice also display abnormal spatial learning and memory whereas CeA-DKO mice have impaired cold-induced thermogenesis. Thus, insulin/IGF-1 signaling has common roles in the hippocampus and central amygdala, affecting synaptic function, systemic glucose homeostasis, behavior, and cognition. In addition, in the hippocampus, insulin/IGF-1 signaling is important for spatial learning and memory whereas insulin/IGF-1 signaling in the central amygdala controls thermogenesis via regulation of neural circuits innervating interscapular brown adipose tissue.
Keywords: amygdala; cognition; hippocampus; insulin; metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: C.R.K. and S.G. are coauthors on a 2016 review article.
Figures

Comment in
-
Unexpected systemic phenotypes result from focal combined deficiencies of forebrain insulin receptor/IGF-1 receptor signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Mar 26;116(13):5852-5854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1901970116. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30858326 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kahn CR, Freychet P, Roth J, Neville DM., Jr Quantitative aspects of the insulin-receptor interaction in liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974;249:2249–2257. - PubMed
-
- Accili D, et al. Early neonatal death in mice homozygous for a null allele of the insulin receptor gene. Nat Genet. 1996;12:106–109. - PubMed
-
- Steele-Perkins G, et al. Expression and characterization of a functional human insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:11486–11492. - PubMed
-
- Liu JP, Baker J, Perkins AS, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r) Cell. 1993;75:59–72. - PubMed
-
- DeChiara TM, Efstratiadis A, Robertson EJ. A growth-deficiency phenotype in heterozygous mice carrying an insulin-like growth factor II gene disrupted by targeting. Nature. 1990;345:78–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

