Pneumatic Tube-Induced Reverse Pseudohyperkalemia in a Patient With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
- PMID: 30766225
- PMCID: PMC6375524
Pneumatic Tube-Induced Reverse Pseudohyperkalemia in a Patient With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
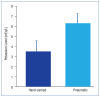
Treatment of reverse pseudohyperkalemia for a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia was complicated by falsely reported elevated potassium levels.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosures The authors report no actual or potential conflicts of interest with regard to this article.
Figures
References
-
- Abraham B, Fakhar I, Tikaria A, et al. Reverse pseudohyperkalemia in a leukemic patient. Clin Chem. 2008;54(2):449–451. - PubMed
-
- Singh PJ, Zawada ET, Santella RN. A case of “reverse” pseudohyperkalemia. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1997;23(1):58–61. - PubMed
-
- Garwicz D, Karlman M. Early recognition of reverse pseudohyperkalemia in heparin plasma samples during leukemic hyperleukocytosis can prevent iatrogenic hypokalemia. Clin Biochem. 2012;45(18):1700–1702. - PubMed
-
- Garwicz D, Karlman M, Øra I. Reverse pseudohyperkalemia in heparin plasma samples from a child with T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with hyperleukocytosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2011;412(3–4):396–397. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources