Health and Economic Burden of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in the United States and Its Impact on Veterans
- PMID: 30766413
- PMCID: PMC6366581
Health and Economic Burden of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in the United States and Its Impact on Veterans
Abstract
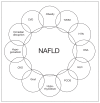
NAFLD is a leading cause of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis in the US and is associated with metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and all-cause mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosures The authors report no actual or potential conflicts of interest with regard to this article.
Figures
References
-
- Targher G, Bertolini L, Padovani R, et al. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its association with cardiovascular disease among type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(5):1212–1218. - PubMed
-
- Targher G, Bertolini L, Rodella S, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is independently associated with an increased prevalence of chronic kidney disease and proliferative/laser-treated retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 2008;51(3):444–450. - PubMed
-
- Loomba R, Sanyal AJ. The global NAFLD epidemic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10(11):686–690. - PubMed
-
- Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64(1):73–84. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
