The Daniel K. Inouye College of Pharmacy Scripts: Perspectives on the Epidemiology of Gout and Hyperuricemia
- PMID: 30766768
- PMCID: PMC6369891
The Daniel K. Inouye College of Pharmacy Scripts: Perspectives on the Epidemiology of Gout and Hyperuricemia
Abstract
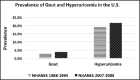
Gout is the most common inflammatory arthritic condition affecting more men than women. Hyperuricemia and the deposition of urate crystals into the joints are the hallmarks of gout. The prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia is rising in the United States and world-wide possibly due to the aging population, comorbidities, and other lifestyle factors. Gout and serum uric acid (SUA) levels are highly heritable, underscoring the role of genetics on disease risk and possibly the racial disparities in gout prevalence. However, high consumption of high fructose corn syrup, alcohol, select dietary lifestyles, and use of diuretics are associated with higher SUA levels and increased risk for developing gout. Adopting healthy diet and lifestyle modifications can lower SUA levels. Nonetheless, diet-based approaches for the management of gout should remain a secondary approach to urate lowering therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Choi HK, Mount DB, Reginato AM American College of P, author. American Physiological S. Pathogenesis of gout. Ann Intern Med. 2005;143(7):499–516. - PubMed
-
- Zhu Y, Pandya BJ, Choi HK. Prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2008. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2011;63(10):3136–3141. - PubMed
-
- Wallace KL, Riedel AA, Joseph-Ridge N, Wortmann R. Increasing prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia over 10 years among older adults in a managed care population. The Journal of Rheumatology. 2004;31(8):1582–1587. - PubMed
-
- Kim JW, Kwak SG, Lee H, Kim SK, Choe JY, Park SH. Prevalence and incidence of gout in Korea: data from the national health claims database 2007–2015. Rheumatology International. 2017;37(9):1499–1506. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical