Once Weekly Dulaglutide Therapy in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects, Real-world Evidence from a Tertiary Care Diabetes Center in India
- PMID: 30766809
- PMCID: PMC6330857
- DOI: 10.4103/ijem.IJEM_424_18
Once Weekly Dulaglutide Therapy in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects, Real-world Evidence from a Tertiary Care Diabetes Center in India
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate the real-world efficacy, durability, and side-effect profile of once weekly GLP1RA: dulaglutide in Indian type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients.
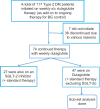
Materials and methods: A retrospective observational study. Data for efficacy (HbA1c and weight), adherence/discontinuation and patient reported side-effects, of 117 patients who were prescribed dulaglutide were analyzed.
Results: Final analysis was done on complete data of 74 patients (6 months follow-up), this indicated that dulaglutide is effective (mean-reduction at 6 months of: HbA1c; 0.87% and weight; 3.8 kg). Subjects with a poorer glycemic control (greater HbA1c) or greater weight at initiation had a better fall in HbA1c and weight reduction at the end of the study. The most common side-effects were gastrointestinal (15% nausea and 6% loose motions). Also, 25% (n = 19) of our study subjects discontinued dulaglutide because of gastrointestinal side-effects.
Conclusion: Our real-world experience is well aligned to systematic data of the randomized controlled trials (RCTs) regarding the efficacy of dulaglutide in the treatment of T2DM (our study vs. RCTs; HbA1c reduction: 0.87% vs. 0.78% to 1.64%, weight reduction: 3.8 vs. 0.3 to 3 kg). The most common side-effects and reason for discontinuation were gastrointestinal side-effects. Finally, by virtue of their observed benefit, we expect a superior cardiovascular risk-reduction with dulaglutide use in our population.
Keywords: Dulaglutide; real-world experience; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- van Dieren S, Beulens JW, van der Schouw YT, Grobbee DE, Neal B. The global burden of diabetes and its complications: An emerging pandemic. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2010;17(Suppl 1):S3–8. - PubMed
-
- Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, Jensen GV, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:383–93. - PubMed
-
- Wysham C, Blevins T, Arakaki R, Colon G, Garcia P, Atisso C, et al. Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide added onto pioglitazone and metformin versus exenatide in type 2 diabetes in a randomized controlled trial (AWARD-1) Diabetes Care. 2014;37:2159–67. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
