Management of Zenker's diverticulum using flexible endoscopy
- PMID: 30766952
- PMCID: PMC6363821
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vgie.2018.12.007
Management of Zenker's diverticulum using flexible endoscopy
Abstract
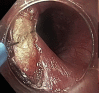
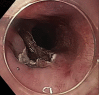
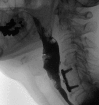
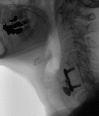
Background and aims: Zenker's diverticulum is a false diverticulum through Killian's dehiscence. Symptoms include halitosis, dysphagia, regurgitation, cough, and aspiration pneumonia. Treatment options include open transcervical cricopharyngeal myotomy, trans-oral rigid endoscopic stapling, and minimally invasive endoscopic myotomy. Although open surgical techniques have historically been the criterion standard for treatment, endoscopic options have become increasingly used. We propose the use of flexible endoscopy in the management of Zenker's diverticulum.
Methods: We present a retrospective case series of 9 patients undergoing endoscopic cricopharyngeal myotomy from 2014 to 2018 using our endoscopic technique.
Results: We demonstrate that endoscopic technique provided adequate symptomatic relief in 7 of 9 patients, with no operative adverse events.
Conclusions: Cricopharyngeal myotomy using flexible endoscopy is a safe and effective technique for the management of Zenker's diverticulum. Potential benefits of this approach include shorter operative times, shorter postoperative admissions, and earlier progression of diet. Initial treatment with endoscopic technique does not preclude future open repairs.
Figures



References
-
- Pescarus R., Shlomovitz E., Sharata A.M. Trans-oral cricomyotomy using a flexible endoscope: technique and clinical outcomes. Surg Endos. 2016;30:1784–1789. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira L.E., Simmons D.T., Baron T.H. Zenker's diverticula: pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and flexible endoscopic management. Dis Esophagus. 2008;21:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Yuan Y., Zhao Y.F., Hu Y. Surgical treatment of Zenker's diverticulum. Dig Surg. 2013;30:207–218. - PubMed
-
- Keck T., Rozsasi A., Grun P.M. Surgical treatment of hypopharyngeal diverticulum (Zenker's diverticulum) Eur Archives of Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;267:587–592. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

