Effects of dapagliflozin vs vildagliptin on cardiometabolic parameters in diabetic patients with coronary artery disease: a randomised study
- PMID: 30767253
- PMCID: PMC6533436
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13903
Effects of dapagliflozin vs vildagliptin on cardiometabolic parameters in diabetic patients with coronary artery disease: a randomised study
Abstract
Aims: Sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors have been shown to reduce cardiovascular events and heart failure in type 2 diabetic (T2D) patients with high cardiovascular risk. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors showed neutral effects and may increase risk of heart failure. We aimed to compare cardiometabolic effects of dapagliflozin and vildagliptin in T2D patients with coronary artery disease (CAD).
Methods: Forty-nine T2D patients with CAD were randomly assigned to dapagliflozin (n = 25) or vildagliptin (n = 24) for 6 months in a double-blind fashion. Cardiometabolic parameters were collected at baseline and at the end of treatments.
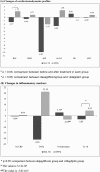
Results: Mean age was 63.2 ± 7.9 years (female 46.9%). Baseline characteristics did not differ between two groups. At 6 months, HbA1C significantly decreased in both dapaglifozin and vildagliptin groups (0.6 ± 1.0% vs 0.8 ± 1.4%, P = 0.22, respectively). There was no difference between the changes in lipid profiles. Body mass index decreased in patients receiving dapagliflozin, whereas it increased in those receiving vildagliptin (-1.27 [95% confidence interval -2.01, -0.53] vs 1.72 [0.72, 2.72] kg, P < 0.001). The reduction in systolic blood pressure and high-sensitivity troponin T was observed in the dapagliflozin group (-9.87 [-18.00, -1.15] mmHg and 2.49 [-4.50, -0.47] pg/mL) but not in vildagliptin group (-1.97 [-9.42, 5.48] mmHg and 1.98 [-0.02, 3.97] pg/mL). The mean haemoglobin increased in the dapagliflozin group, whereas the mean platelet volume increased in the vildagliptin group. There was no significant change in the inflammatory markers in both the groups.
Conclusions: The extraglycaemic effects of dapagliflozin and vildagliptin on cardiometabolic parameters in T2D with CAD were different. The more favourable effects of dapagliflozin compared to vildagliptin may have explained the cardiovascular benefits observed only in sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors.
Keywords: coronary artery disease; dapagliflozin; diabetes; dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors; sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors; vildagliptin.
© 2019 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Tancredi M, Rosengren A, Svensson AM, et al. Excess mortality among persons with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(18):1720‐1732. - PubMed
-
- Haffner SM, Lehto S, Ronnemaa T, Pyorala K, Laakso M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(4):229‐234. - PubMed
-
- Gaede P, Vedel P, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Intensified multifactorial intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: the Steno type 2 randomised study. Lancet. 1999;353(9153):617‐622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous