Roles of the ClpX IGF loops in ClpP association, dissociation, and protein degradation
- PMID: 30767302
- PMCID: PMC6423715
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3590
Roles of the ClpX IGF loops in ClpP association, dissociation, and protein degradation
Abstract
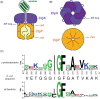
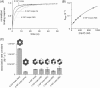
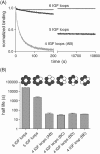
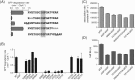
IGF-motif loops project from the hexameric ring of ClpX and are required for docking with the self-compartmentalized ClpP peptidase, which consists of heptameric rings stacked back-to-back. Here, we show that ATP or ATPγS support assembly by changing the conformation of the ClpX ring, bringing the IGF loops closer to each other and allowing efficient multivalent contacts with docking clefts on ClpP. In single-chain ClpX pseudohexamers, deletion of one or two IGF loops modestly slows association with ClpP but strongly accelerates dissociation of ClpXP complexes. We probe how changes in the sequence and length of the IGF loops affect ClpX-ClpP interactions and show that deletion of one or two IGF loops slows ATP-dependent proteolysis by ClpXP. We also find that ClpXP degradation is less processive when two IGF loops are deleted.
Keywords: AAA+ protease; ATP-fueled molecular machine; kinetics; protein degradation.
© 2019 The Protein Society.
Figures


References
-
- Sauer RT, Baker TA (2011) AAA+ proteases: ATP‐fueled machines of destruction. Annu Rev Biochem 80:587–612. - PubMed
-
- Flynn JM, Neher SB, Kim YI, Sauer RT, Baker TA (2003) Proteomic discovery of cellular substrates of the ClpXP protease reveals five classes of ClpX‐recognition signals. Mol Cell 11:671–683. - PubMed
-
- Moore SD, Sauer RT (2007) The tmRNA system for translational surveillance and ribosome rescue. Annu Rev Biochem 76:101–124. - PubMed
-
- Keiler KC (2008) Biology of trans‐translation. Annu Rev Microbiol 62:133–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

