Persistence of antibiotic resistance genes in beef cattle backgrounding environment over two years after cessation of operation
- PMID: 30768641
- PMCID: PMC6377141
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212510
Persistence of antibiotic resistance genes in beef cattle backgrounding environment over two years after cessation of operation
Abstract
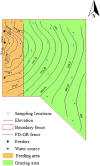
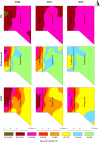
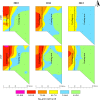
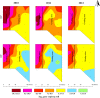
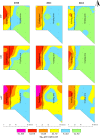
Confined animal feeding operations can facilitate the spread of genes associated with antibiotic resistance. It is not known how cattle removal from beef cattle backgrounding operation affects the persistence of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in the environment. We investigated the effect of cessation of beef cattle backgrounding operation on the persistence and distribution of ARGs in the beef cattle backgrounding environment. The study was conducted at a pasture-feedlot type beef cattle backgrounding operation which consisted of feeding and grazing areas that were separated by a fence with an access gate. Backgrounding occurred for seven years before cattle were removed from the facility. Soil samples (n = 78) from 26 georeferenced locations were collected at the baseline before cattle were removed, and then one year and two years after cattle were removed. Metagenomic DNA was extracted from the soil samples and total bacterial population (16S rRNA), total Enterococcus species and class 1 integrons (intI1), and erythromycin (ermB and ermF), sulfonamide (sul1 and sul2) and tetracycline (tetO, tetW and tetQ) resistance genes were quantified. Concentrations of total bacteria, Enterococcus spp., class 1 integrons, and ARGs were higher in the feeding area and its immediate vicinity (around the fence and the gate) followed by a gradient decline along the grazing area. Although the concentrations of total bacteria, Enterococcus spp., class 1 integrons and ARGs in the feeding area significantly decreased two years after cattle removal, their concentrations were still higher than that observed in the grazing area. Higher concentrations over two years in the feeding area when compared to the grazing area suggest a lasting effect of confined beef cattle production system on the persistence of bacteria and ARGs in the soil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- FDA. Guidance for Industry # 152: Evaluating the safety of antimicrobial new animal drugs with regard to their microbiological effects on bacteria of human health concern. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Center for Veterinary Medicine, Rockville, MD. 2003.
-
- FDA. Guidance For Industry #213: New animal drugs and new animal drug combination products administered in or on medicated feed or drinking water of food producing animals: Recommendations for drug sponsors for voluntarily aligning product use conditions with GFI #209. 2013. Center for Veterinary Medicine. Food and Drug Admisitration (FDA). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2013.
-
- FDA. 2016 Summary report on antimicrobials sold or distributed for use in food-producing animals. Cenetr for Veterinary Medicine, U.S. Food and Drug Adminstration (FDA), Department of Health and Human Services. 2017.
-
- FDA. Judicious use guidance, GFI #209: The judicious use of medically important antimicrobial drugs in food-producing animals. 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

