THO Complex Subunit 7 Homolog Negatively Regulates Cellular Antiviral Response against RNA Viruses by Targeting TBK1
- PMID: 30769920
- PMCID: PMC6410154
- DOI: 10.3390/v11020158
THO Complex Subunit 7 Homolog Negatively Regulates Cellular Antiviral Response against RNA Viruses by Targeting TBK1
Abstract
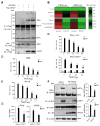
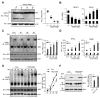
RNA virus invasion induces a cytosolic RIG-I-like receptor (RLR) signaling pathway by promoting assembly of the Mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS) signalosome and triggers the rapid production of type I interferons (IFNs) and proinflammatory cytokines. During this process, the pivotal kinase TANK binding kinase 1 (TBK1) is recruited to the MAVS signalosome to transduce a robust innate antiviral immune response by phosphorylating transcription factors interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) and nuclear factor (NF)-κB and promoting their nuclear translocation. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the negative regulation of TBK1 are largely unknown. In the present study, we found that THO complex subunit 7 homolog (THOC7) negatively regulated the cellular antiviral response by promoting the proteasomal degradation of TBK1. THOC7 overexpression potently inhibited Sendai virus- or polyI:C-induced IRF3 dimerization and phosphorylation and IFN-β production. In contrast, THOC7 knockdown had the opposite effects. Moreover, we simulated a node-activated pathway to show that THOC7 regulated the RIG-I-like receptors (RLR)-/MAVS-dependent signaling cascade at the TBK1 level. Furthermore, THOC7 was involved in the MAVS signalosome and promoted TBK1 degradation by increasing its K48 ubiquitin-associated polyubiquitination. Together, these findings suggest that THOC7 negatively regulates type I IFN production by promoting TBK1 proteasomal degradation, thus improving our understanding of innate antiviral immune responses.
Keywords: MAVS signalosome; TBK1; THOC7; cellular antiviral response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

