Development of a clinical practice guideline for orthodontic retention
- PMID: 30771260
- PMCID: PMC6850190
- DOI: 10.1111/ocr.12302
Development of a clinical practice guideline for orthodontic retention
Abstract
Objectives: To develop a clinical practice guideline (CPG) for orthodontic retention (OR).
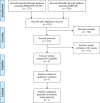
Materials and methods: The CPG was developed according to the AGREE II instrument and EBRO (Dutch methodology for evidence-based guideline development). Reporting was done according the RIGHT statement. A Task Force developed clinical questions regarding OR. To answer these questions, a systematic literature search in PubMed and EMBASE was performed. Two independent researchers identified and selected studies, assessed risk of bias using Cochrane RoB tool and rated quality of evidence using GRADE. The Task Force formulated considerations and recommendations after discussing the evidence. The concept CPG was sent for commentary to all relevant stakeholders.
Result: One systematic review-with 15 studies-met the inclusion criteria. In case of low evidence and lack of outcome measures, expert-based considerations were developed. Over four meetings, the Task Force reached consensus on considerations and recommendations, after which the concept CPG was ready for the commentary phase. After processing the comments, the CPG was presented to the Dutch Association of Orthodontists, whereafter authorization followed.
Limitations: The paucity of evidence-based studies concerning OR and the reporting of measurable patient outcomes.
Conclusion: This CPG offers practitioner recommendations for best practice regarding OR, may reduce variation between practices and assists with patient aftercare. A carefully chosen retention procedure for individual patients, combined with clear information and communication between orthodontist, dentist and patient will contribute to long-term maintenance of orthodontic treatment results.
Keywords: clinical practice guideline; orthodontic; retention.
© 2019 The Authors. Orthodontics & Craniofacial Research Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
According to the “Code for the prevention of improper influence due to conflicts of interest” (
Figures
References
-
- Maltha J, Hoff von den J. Biological basis for orthodontic relapse In: Katsaros C, Eliades T. eds. Stability, retention & relapse in orthodontics. 1st edn, Deutschland: Quintessence Publishing; 2017:15‐25. ISBN: 978‐1‐78698‐019‐9.
-
- Vaden L, Harris EF, Gardner RL. Relapse revisited. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 1997;111(5):543‐553. - PubMed
-
- Thilander B. Orthodontic relapse versus natural development. Am J Dentofacial Orthop. 2000;117(5):562‐563. - PubMed
-
- Littlewood SJ. Retention In: Mitchell L. ed. An introduction to orthodontics, 4th edn Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 2013:193‐207. ISBN 978‐0‐19‐959471‐9.
-
- Padmos JAD, Fudalej PS, Renkema AM. Epidemiologic study of orthodontic retention procedures. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2018;153(4):496‐504. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous