Squalamine blocks tumor-associated angiogenesis and growth of human breast cancer cells with or without HER-2/neu overexpression
- PMID: 30771431
- PMCID: PMC6598711
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.02.009
Squalamine blocks tumor-associated angiogenesis and growth of human breast cancer cells with or without HER-2/neu overexpression
Abstract
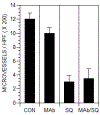
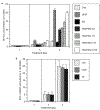
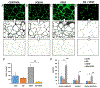
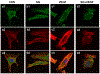
Angiogenesis is critical for breast cancer progression. Overexpression of HER-2/neu receptors occur in 25-30% of breast cancers, and treatment with trastuzumab inhibits HER-2-overexpressing tumor growth. Notably, HER-2-mediated signaling enhances vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion to increase tumor-associated angiogenesis. Squalamine (aminosterol compound) suppresses VEGF-induced activation of kinases in vascular endothelial cells and inhibits tumor-associated angiogenesis. We assessed antitumor effects of squalamine either alone or with trastuzumab in nude mice bearing breast tumor xenografts without (MCF-7) or with HER2-overexpression (MCF-7/HER-2). Squalamine alone inhibited progression of MCF-7 tumors lacking HER2 overexpression, and squalamine combined with trastuzumab elicited marked inhibition of MCF-7/HER2 growth exceeding that of trastuzumab alone. MCF-7/HER-2 cells secrete higher levels of VEGF than MCF-7 cells, but squalamine elicited no growth inhibition of either MCF-7/HER-2 or MCF-7 cells in vitro. However, squalamine did stop growth of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and reduced VEGF-induced endothelial tube-like formations in vitro. These effects correlated with blockade of focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation and stress fiber assembly in HUVECs. Thus, squalamine effectively inhibits growth of breast cancers with or without HER-2-overexpression, an effect due in part to blockade of tumor-associated angiogenesis.
Keywords: Breast cancer; MCF-7; Squalamine; Trastuzumab; Tumor-associated angiogenesis; VEGF.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Richard J. Pietras has consulted with Astra-Zeneca, Pfizer and Genentech. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
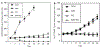
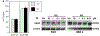

References
-
- Coussens L, Yang-Feng TL, Liao YC, Chen E, Gray A, McGrath J, Seeburg PH, Libermann TA, Schlessinger J, Francke U, et al., Tyrosine kinase receptor with extensive homology to EGF receptor shares chromosomal location with neu oncogene, Science 230(4730) (1985) 1132–1139. - PubMed
-
- Harris JR, Lippman ME, Veronesi U, Willett W, Breast cancer (3), N Engl J Med 327(7) (1992) 473–480. - PubMed
-
- Lemoine NR, Staddon S, Dickson C, Barnes DM, Gullick WJ, Absence of activating transmembrane mutations in the c-erbB-2 proto-oncogene in human breast cancer, Oncogene 5(2) (1990) 237–239. - PubMed
-
- Press MF, Slamon DJ, Flom KJ, Park J, Zhou JY, Bernstein L, Evaluation of HER-2/neu gene amplification and overexpression: comparison of frequently used assay methods in a molecularly characterized cohort of breast cancer specimens, J Clin Oncol 20(14) (2002) 3095–3105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

