Standards for MIC testing that apply to the majority of bacterial pathogens should also be enforced for Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex
- PMID: 30771527
- PMCID: PMC7903878
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.01.019
Standards for MIC testing that apply to the majority of bacterial pathogens should also be enforced for Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex
Keywords: MIC testing; Microtiter plates; Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex; Quality control ranges; Quality control targets.
Figures
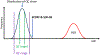
References
-
- World Health Organization. Technical report on critical concentrations for drug susceptibility testing of medicines used in the treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis [WHO/CDS/TB/2018.5]. Available at: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/260470/1/WHO-CDS-TB-2018.5-eng.pdf (accessed 19 December 2018).
-
- Kahlmeter G The 2014 Garrod Lecture: EUCAST ‒ are we heading towards international agreement? J Antimicrob Chemother 2015;70:2427–39. - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. M23. Development of in vitro susceptibility testing criteria and quality control parameters. 5th ed Wayne, PA: CLSI; 2018.
-
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Routine and extended internal quality control for MIC determination and disk diffusion as recommended by EUCAST. Version 8.0. 2018. Available at: http://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/QC/v_8.0_EUC... (accessed 19 September 2018).
-
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 20776-2:2007. Clinical laboratory testing and in vitro diagnostic test systems — susceptibility testing of infectious agents and evaluation of performance of antimicrobial susceptibility test devices — Part 2: evaluation of performance of antimicrobial susceptibility test devices. 1st ed Geneva: ISO; 2007.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

