ERK Inhibitor Enhances Everolimus Efficacy through the Attenuation of dNTP Pools in Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 30771617
- PMCID: PMC6374702
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.01.001
ERK Inhibitor Enhances Everolimus Efficacy through the Attenuation of dNTP Pools in Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
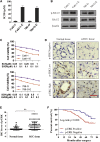
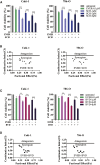
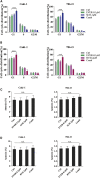
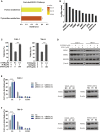
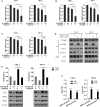
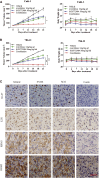
The clinical efficiency of everolimus, an mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor, is palliative as sequential or second-line therapy for renal cell carcinoma (RCC). However, the limited response of everolimus in RCC remains uncertain. In the present study, everolimus-resistant RCC models were established to understand the mechanisms and to seek combination approaches. Consequently, the activation of ERK was found to contribute toward everolimus-acquired resistance and poor prognosis in patients with RCC. In addition, the efficacy and mechanism of combination treatment underlying RCC using everolimus and ERK inhibitors was investigated. The ERK inhibitor in combination with everolimus synergistically inhibited the proliferation of RCC cells by arresting the cell cycle in the G1 phase. The combination treatment markedly attenuated the deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) pools by downregulating the mRNA expression of RRM1 and RRM2 through E2F1. The overexpression of E2F1 or supplementation of dNTP rescued the anti-proliferation activity of the everolimus-SCH772984 combination. The antitumor efficacy of combination therapy was reiterated in RCC xenograft models. Thus, the current findings provided evidence that the everolimus-ERK inhibitor combination is a preclinical therapeutic strategy for RCC.
Keywords: ERK inhibitor; dNTP; everolimus; renal cell carcinoma; ribonucleotide reductase.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The selective MEK1 inhibitor Selumetinib enhances the antitumor activity of everolimus against renal cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 28;8(13):20825-20833. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15346. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28212559 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Inhibition of mTOR and Bcl-2 Enhances the Anti-tumor Effect of Everolimus against Renal Cell Carcinoma In Vitro and In Vivo.J Cancer. 2019 Feb 23;10(6):1466-1478. doi: 10.7150/jca.29192. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31031856 Free PMC article.
-
The preclinical assessment of XL388, a mTOR kinase inhibitor, as a promising anti-renal cell carcinoma agent.Oncotarget. 2017 May 2;8(18):30151-30161. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15620. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28404914 Free PMC article.
-
Everolimus in the management of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: an evidence-based review of its place in therapy.Core Evid. 2016 Sep 1;11:23-36. doi: 10.2147/CE.S98687. eCollection 2016. Core Evid. 2016. PMID: 27621699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Everolimus in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma and neuroendocrine tumors.Adv Ther. 2010 Aug;27(8):495-511. doi: 10.1007/s12325-010-0045-2. Epub 2010 Jul 8. Adv Ther. 2010. PMID: 20623346 Review.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of Peroxiredoxin-2 in Well-Differentiated Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors and Its Utility as a Biomarker for Predicting the Response to Everolimus.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Nov 9;9(11):1104. doi: 10.3390/antiox9111104. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33182509 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Immune-Related Subtypes and Characterization of Tumor Microenvironment Infiltration in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Jun 29;13:906113. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.906113. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35846133 Free PMC article.
-
The therapeutic value of SC66 in human renal cell carcinoma cells.Cell Death Dis. 2020 May 11;11(5):353. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2566-1. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32393791 Free PMC article.
-
ERK Inhibitor Ulixertinib Inhibits High-Risk Neuroblastoma Growth In Vitro and In Vivo.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 10;14(22):5534. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225534. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428626 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel and potent dual-targeting HDAC1/SPOP inhibitors using structure-based virtual screening, molecular dynamics simulation and evaluation of in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 10;14:1208740. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1208740. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37492092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fisher R., Gore M., Larkin J. Current and future systemic treatments for renal cell carcinoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013;23:38–45. - PubMed
-
- Motzer R.J., Escudier B., Oudard S., Hutson T.E., Porta C., Bracarda S., Grünwald V., Thompson J.A., Figlin R.A., Hollaender N., RECORD-1 Study Group Phase 3 trial of everolimus for metastatic renal cell carcinoma : final results and analysis of prognostic factors. Cancer. 2010;116:4256–4265. - PubMed
-
- Czarnecka A.M., Kornakiewicz A., Lian F., Szczylik C. Future perspectives for mTOR inhibitors in renal cell cancer treatment. Future Oncol. 2015;11:801–817. - PubMed
-
- Motzer R.J., Hutson T.E., Glen H., Michaelson M.D., Molina A., Eisen T., Jassem J., Zolnierek J., Maroto J.P., Mellado B. Lenvatinib, everolimus, and the combination in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, phase 2, open-label, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:1473–1482. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

