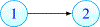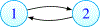Local immunodeficiency: Minimal networks and stability
- PMID: 30772457
- PMCID: PMC6474679
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mbs.2019.02.002
Local immunodeficiency: Minimal networks and stability
Abstract
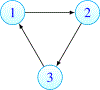
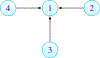
Some basic aspects of the recently discovered phenomenon of local immunodeficiency (Skums et al. [1]) generated by antigenic cooperation in cross-immunoreactivity (CR) networks are investigated. We prove that local immunodeficiency (LI) that is stable under perturbations already occurs in very small networks and under general conditions on their parameters. Therefore our results are applicable not only to Hepatitis C where CR networks are known to be large (Skums et al. [1]), but also to other diseases with CR. A major necessary feature of such networks is the non-homogeneity of their topology. It is also shown that one can construct larger CR networks with stable LI by using small networks with stable LI as their building blocks. Our results imply that stable LI occurs in networks with quite general topology. In particular, the scale-free property of a CR network, assumed in Skums et al. [1], is not required.
Keywords: Cross-immunoreactivity network; Local immunodeficiency; Minimal stable network.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Hattori M, Yashioka K, Aiyama T, Iwata K, Terazawa Y, Ishigami M, Yano M, Kakumu S, Broadly reactive antibodies to hypervariable region 1 in hepatitis C virus-infected patient sera: relation to viral loads and response to interferon, Hepatology 27 (6) (1998) 1703–1710. - PubMed
-
- Nowak MA, May RM, Virus Dynamics: Mathematical Principles of Immunology and Virology, Oxford University Press, 2000.
-
- Yoshioka K, Aiyama T, Okumura A, Takayanagi M, Iwata K, Ishikawa T, Nagai Y, Kakumu S, Humoral Immune Response to the Hypervariable Region of Hepatitis C Virus Differs between Genotypes 1b and 2a, The Journal of Infectious Diseases 175 (3) (1997) 505–510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical