Cognitive Decline in Older Patients With Non- ST Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome
- PMID: 30773118
- PMCID: PMC6405683
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011218
Cognitive Decline in Older Patients With Non- ST Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome
Abstract
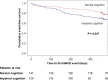
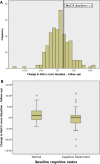
Background Dementia is a growing health burden of an aging population. This study aims to evaluate the prevalence of cognitive impairment and the predictors of cognitive decline at 1 year in older patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome undergoing invasive care. Methods and Results Older patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome were recruited into the ICON1 study. Cognition was evaluated using Montreal Cognitive Assessment. The composite major adverse cardiovascular events comprised death, myocardial infarction, unplanned revascularization, stroke, and significant bleeding at 1 year. Of 298 patients, 271 had cognitive assessment at baseline, and 211 (78%) had follow-up Montreal Cognitive Assessment at 1 year. Mean age was 80.5±4.8 years. There was a high prevalence (n=130, 48.0%) of undiagnosed cognitive impairment (Montreal Cognitive Assessment score <26) at baseline. Cognitive impairment patients were more likely to reach major adverse cardiovascular events by Kaplan-Meier analysis ( P=0.047). Seventy-four patients (35.1%) experienced cognitive decline (Montreal Cognitive Assessment score drop by ≥2 points) at 1 year. Recurrent myocardial infarction was independently associated with cognitive decline at 1 year (odds ratio 3.19, 95% confidence interval 1.18-8.63, P=0.02) after adjustment for age and sex. Conclusions In older patients undergoing invasive management of non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome, there is a high prevalence of undiagnosed cognitive impairment at baseline. Recurrent myocardial infarction is independently associated with cognitive decline at 1 year. Clinical Trial Registration URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov . Unique identifier: NCT01933581.
Keywords: cognition; cognitive impairment; coronary artery disease; non‐ST‐segment–elevation acute coronary syndrome.
Figures

Comment in
-
Rethinking Cognitive Impairment in the Management of Older Patients With Cardiovascular Disease.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Feb 19;8(4):e011968. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.011968. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 30773969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fowkes R, Byrne M, Sinclair H, Tang E, Kunadian V. Coronary artery disease in patients with dementia. Coron Artery Dis. 2016;27:511–520. - PubMed
-
- Newman AB, Fitzpatrick AL, Lopez O, Jackson S, Lyketsos C, Jagust W, Ives D, DeKosky ST, Kuller LH. Dementia and Alzheimer's disease incidence in relationship to cardiovascular disease in the Cardiovascular Health Study cohort. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53:1101–1107. - PubMed
-
- Aronson MK, Ooi WL, Morgenstern H, Hafner A, Masur D, Crystal H, Frishman WH, Fisher D, Katzman R. Women, myocardial infarction, and dementia in the very old. Neurology. 1990;40:1102–1106. - PubMed
-
- Justin Zaman M, Stirling S, Shepstone L, Ryding A, Flather M, Bachmann M, Myint PK. The association between older age and receipt of care and outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes: a cohort study of the Myocardial Ischaemia National Audit Project (MINAP). Eur Heart J. 2014;35:1551–1558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

