Qingxin kaiqiao fang ameliorates memory impairment and inhibits apoptosis in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice through the MAPK pathway
- PMID: 30774310
- PMCID: PMC6350643
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S188505
Qingxin kaiqiao fang ameliorates memory impairment and inhibits apoptosis in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice through the MAPK pathway
Abstract
Background: Qingxin kaiqiao fang (QKF) has been found to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD) through apoptosis inhibition. The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is closely related to apoptosis in the course of AD. This study aimed to investigate whether QKF-induced apoptosis depression is achieved through MAPK pathway.
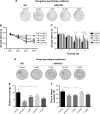
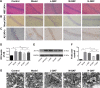
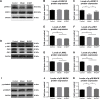
Materials and methods: C57BL/6 J and APP/PS1 mice were used as control and model groups. APP/PS1 mice were treated with different dosages of QKF (4.75, 9.5, and 19 g⋅kg-1⋅d-1⋅ig, respectively) for 12 weeks as L-QKF, M-QKF, and H-QKF groups. The M-QKF-treated APP/ PS1 mice were administrated with 2 µg/kg of U46619 and saline, intra ventricular ventricle injection, as M-QKF+U46619 and M-QKF+saline groups and were injected with PD98059 0.3 mg/kg and the same volume of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), intravenous, as M-QKF+PD98059 and M-QKF+DMSO groups. After 12 weeks treatment, Morris water maze was performed for behavior study. Pathological degeneration was examined by H&E staining, Nissl staining, and transmission electron microscope observation of hippocampus; immunohistochemistry and Western blot (WB) were tested for amyloid β (Aβ) expression. Apoptosis was measured through TUNEL assay; Bax, Bcl-2, and caspase-3 expression through WB; and cleaved caspase-3 expression through ELISA. MAPK pathway was detected via WB for the expressions of ERK1/2, JNK, and p38 MAPK and their phosphorylation patterns.
Results: QKF improved the learning and memory capability, as well as inhibited neuronal apoptosis and then reduced the pathological degeneration of APP/PS1 mice. M-QKF reduced neuron apoptosis by inhibiting p38 MAPK and activating ERK1/2 but had no significant effect on JNK.
Conclusion: QKF, especially at the middle dose, alleviated the learning and memory impairment and played an antiapoptotic role in AD through MAPK pathways.
Keywords: APP; Alzheimer’s disease; MAPK; PS1 mice; Qingxin kaiqiao; apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Qingxin Kaiqiao Fang decreases Tau hyperphosphorylation in Alzheimer's disease via the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway in vitro and in vivo.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 10;318(Pt B):117031. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117031. Epub 2023 Aug 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37579924
-
Qingxin Kaiqiao Fang Inhibits Aβ 25-35-Induced Apoptosis in Primary Cultured Rat Hippocampal Neuronal Cells via the p38 MAPK Pathway: An Experimental Validation and Network Pharmacology Study.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Aug 3;2020:9058135. doi: 10.1155/2020/9058135. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32831882 Free PMC article.
-
Dengzhan Shengmai capsule ameliorates cognitive impairment via inhibiting ER stress in APP/PS1 mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Feb 10;338(Pt 1):119016. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119016. Epub 2024 Nov 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39505222
-
Lancao decoction in the treatment of alzheimer's disease via activating PI3K/AKT signaling to promote ERK involving in enhancing neuronal activities in the hippocampus.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Feb 10;338(Pt 1):119017. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119017. Epub 2024 Nov 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39528121
-
CART modulates beta-amyloid metabolism-associated enzymes and attenuates memory deficits in APP/PS1 mice.Neurol Res. 2017 Oct;39(10):885-894. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2017.1348689. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Neurol Res. 2017. PMID: 28743230
Cited by
-
Dexmedetomidine Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Hippocampal Neuronal Apoptosis via Inhibiting the p38 MAPK/c-Myc/CLIC4 Signaling Pathway in Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Nov;58(11):5533-5547. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02512-9. Epub 2021 Aug 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34363182
-
MiR-191-5p alleviates microglial cell injury by targeting Map3k12 (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 12) to inhibit the MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) signaling pathway in Alzheimer's disease.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):12678-12690. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2008638. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34818971 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated approach with UHPLC-Q-Exactive-tandem mass spectrometry, network analysis, and molecular docking to determine potential active compounds and mechanisms of Rhizoma Musae decoction in osteoarthritis treatment.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 2;15:1380335. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1380335. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39822742 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered macrophage-biomimetic versatile nanoantidotes for inflammation-targeted therapy against Alzheimer's disease by neurotoxin neutralization and immune recognition suppression.Bioact Mater. 2023 Mar 15;26:337-352. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.03.004. eCollection 2023 Aug. Bioact Mater. 2023. PMID: 36950153 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Analysis of miRNAs and mRNAs Network-Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction Exerts Neuroprotection of Traumatic Brain Injury Mice in the Subacute Phase.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 22;13:772680. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.772680. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35814248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Courtney C, Farrell D, Gray R, et al. Long-term donepezil treatment in 565 patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD2000): randomised double-blind trial. Lancet. 2004;363(9427):2105–2115. - PubMed
-
- Panagaki T, Gengler S, Hölscher C. The novel DA-CH3 dual incretin restores endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy impairments to attenuate Alzheimer-like pathology and cognitive decrements in the APPSWE/PS1ΔE9 mouse model. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;66(1):195–218. - PubMed
-
- Anantha Krishnan D, Gunasekaran K, Iqbal S. Identification of potential PKC inhibitors through pharmacophore designing, 3D-QSAR and molecular dynamics simulations targeting Alzheimer’s disease. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2017;13:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Ryu J, Yu HN, Cho H, et al. Neuregulin-1 exerts protective effects against neurotoxicities induced by C-terminal fragments of APP via ErbB4 receptor. J Pharmacol Sci. 2012;119(1):73–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

