Leptin resistance: underlying mechanisms and diagnosis
- PMID: 30774404
- PMCID: PMC6354688
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S182406
Leptin resistance: underlying mechanisms and diagnosis
Abstract
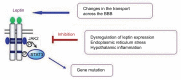
Leptin and its receptors have been identified as key regulators of body weight and energy homeostasis. A decrease in tissue sensitivity to leptin leads to the development of obesity and metabolic disorders, such as insulin resistance and dyslipidemia. Mechanisms underlying the development of leptin resistance include mutations in the genes encoding leptin and its receptors, as well as proteins involved in self-regulation of leptin synthesis and blood-brain barrier permeability. Leptin resistance encompasses a complex pathophysiological phenomenon with a number of potential research lines. In this review, we analyze the existing data on the methods used to diagnose leptin resistance.
Keywords: leptin; leptin resistance; soluble leptin receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Morioka T, Mori K, Motoyama K, Emoto M. Ectopic fat accumulation and glucose homeostasis: role of leptin in glucose and lipid metabolism and mass maintenance in skeletal muscle. In: Inaba M, editor. Musculoskeletal Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus. Tokyo: Springer Japan; 2016. pp. 201–213.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

