Myelin basic protein charge isomers change macrophage polarization
- PMID: 30774410
- PMCID: PMC6350649
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S189570
Myelin basic protein charge isomers change macrophage polarization
Abstract
Purpose: During a neuronal injury, a variety of immune cells infiltrate into the local microenvironment at the demyelination site. After the destruction of the intact myelin sheath, its major constituent myelin basic protein (MBP) dissociates from the plasma membrane and acts as a free ligand on the infiltrated immune cells. MBP exhibits charge microheterogeneity as a result of post-translational modifications, but the effect of various isomers of MBP on the activity of macrophages is not known.
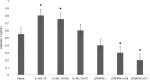
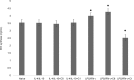
Materials and methods: MBP was isolated and purified from bovine brain white matter. RAW 264.7 macrophages were cultured in DMEM supplemented with heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum. For evaluation of macrophage polarization following treatment of RAW 264.7 cells with MBP charge isomers, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression (M1 phenotype marker) and arginase-1 expression (M2 phenotype marker) were determined in cell lysates by ELISA. To assess Rac activity, G-LISA Rac Activation Assay system was used. The expression of receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) and high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein were assayed by Western blot analysis.
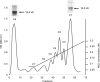
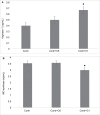
Results: Our results have shown that minimally modified C1 component of MBP increases the expression of arginase-1 in cells, decreases the expression of iNOS, does not change the secretion of HMGB1 protein, but significantly elevates surface expression of RAGE, and in parallel, increases the activity of small GTPase Rac. On the other hand, highly modified deiminated isomer C8-MBP increases the secretion of HMGB1 protein but does not change the expression of arginase-1 or the content of RAGE.
Conclusion: These data indicate that deiminated C8 isomer of MBP tends to polarize RAW macrophages into M1 phenotypes, whereas C1 enhances the activity of M2 phenotype markers.
Keywords: Arginase-1; HMGB1; RAGE; iNOS.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Citrullinated isomer of myelin basic protein can induce inflammatory responses in astrocytes.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2023 Dec 19;16:127-134. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2023.12.003. eCollection 2024 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38288135 Free PMC article.
-
HMGB1 enhances the protumoral activities of M2 macrophages by a RAGE-dependent mechanism.Tumour Biol. 2016 Mar;37(3):3321-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3940-y. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26440051
-
[Effect of Galectin-9/Tim-3 pathway on the polarization of M1/M2 subtype in murine macrophages induced by lipopolysaccharide].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Sep;30(9):836-841. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.09.004. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 30309408 Chinese.
-
Skewed Signaling through the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products Alters the Proinflammatory Profile of Tumor-Associated Macrophages.Cancer Microenviron. 2018 Dec;11(2-3):97-105. doi: 10.1007/s12307-018-0214-4. Epub 2018 Aug 8. Cancer Microenviron. 2018. PMID: 30091031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolism via Arginase or Nitric Oxide Synthase: Two Competing Arginine Pathways in Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2014 Oct 27;5:532. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00532. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25386178 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Citrullinated isomer of myelin basic protein can induce inflammatory responses in astrocytes.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2023 Dec 19;16:127-134. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2023.12.003. eCollection 2024 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38288135 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signaling modulates macrophage polarization and is regulated by biomaterial surface properties.Biomaterials. 2020 Jun;243:119920. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.119920. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Biomaterials. 2020. PMID: 32179303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zand R, Jin X, Kim J, Wall DB, Gould R, Lubman DM. Studies of posttranslational modifications in spiny dogfish myelin basic protein. Neurochem Res. 2001;26(5):539–547. - PubMed
-
- Wood DD, Moscarello MA. The isolation, characterization, and lipid-aggregating properties of a citrulline containing myelin basic protein. J. Biol Chem. 1989;264:5121–5127. - PubMed
-
- Fannon AM, Moscarello MA. Characterization of myelin basic protein charge isomers from adult mouse brain. Neuro report. 1991;2(3):135–138. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

