Optimal management of glenohumeral osteoarthritis
- PMID: 30774456
- PMCID: PMC6209346
- DOI: 10.2147/ORR.S134732
Optimal management of glenohumeral osteoarthritis
Abstract
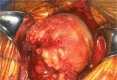
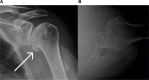
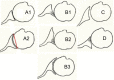
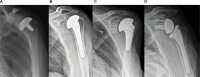
Glenohumeral osteoarthritis (OA) is defined as progressive loss of articular cartilage, resulting in bony erosion, pain, and decreased function. This article provides a gross overview of this disease, along with peer-reviewed research by experts in the field. The pathology, diagnosis, and classification of this condition have been well described. Treatment begins with non-operative measures, including oral and topical anti-inflammatory agents, physical therapy, and intra- articular injections of either a corticosteroid or a viscosupplementation agent. Operative treatment is based on the age and function of the affected patient, and treatment of young individuals with glenohumeral OA remains controversial. Various methods of surgical treatment, ranging from arthroscopy to resurfacing, are being evaluated. The roles of hemiarthroplasty, total shoulder arthroplasty, and reverse shoulder arthroplasty are similarly reviewed with supporting data.
Keywords: glenohumeral; hemiarthroplasty; hyaluronic acid; osteoarthritis; total shoulder arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Kobayashi T, Takagishi K, Shitara H, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for shoulder osteoarthritis in Japanese middle-aged and elderly populations. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(5):613–619. - PubMed
-
- Oh JH, Chung SW, Oh CH, et al. The prevalence of shoulder osteoarthritis in the elderly Korean population: association with risk factors and function. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(5):756–763. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

