A tribute to Dr. Saul Hertz: The discovery of the medical uses of radioiodine
- PMID: 30774539
- PMCID: PMC6357704
- DOI: 10.4103/wjnm.WJNM_107_18
A tribute to Dr. Saul Hertz: The discovery of the medical uses of radioiodine
Abstract
Dr. Saul Hertz was Director of The Massachusetts General Hospital's Thyroid Unit, when he heard about the development of artificial radioactivity. He conceived and brought from bench to bedside the successful use of radioiodine (RAI) to diagnose and treat thyroid diseases. Thus was born the science of theragnostics used today for neuroendorine tumors and prostate cancer. Dr. Hertz's work set the foundation of targeted precision medicine.
Keywords: Dr. Saul Hertz; nuclear medicine; radioiodine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


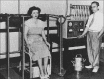

References
-
- Hertz S, Roberts A. Radioactive iodine in the study of thyroid physiology. VII The use of radioactive iodine therapy in hyperthyroidism. J Am Med Assoc. 1946;131:81–6. - PubMed
-
- Hertz S. A plan for analysis of the biologic factors involved in experimental carcinogenesis of the thyroid by means of radioactive isotopes. Bull New Engl Med Cent. 1946;8:220–4. - PubMed
-
- Thrall J. The Story of Saul Hertz, Radioiodine and the Origins of Nuclear Medicine. [Last accessed on 2018 Dec 01]. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=34Qhm8CeMuc .
-
- Braverman L. 131 Iodine Therapy: A Brief History. [Last accessed on 2018 Dec 01]. Available from: http://www.am2016.aace.com/presentations/friday/F12/hertz_braverman.pdf .
-
- Hofman MS, Violet J, Hicks RJ, Ferdinandus J, Thang SP, Akhurst T, et al. [177Lu]-PSMA-617 radionuclide treatment in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (LuPSMA trial): A single-centre, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:825–33. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

