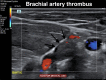
Diagnosis of Brachial Artery Thromboembolism with Point-of-care Ultrasound
- PMID: 30775678
- PMCID: PMC6366392
- DOI: 10.5811/cpcem.2019.1.41181
Diagnosis of Brachial Artery Thromboembolism with Point-of-care Ultrasound
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: By the CPC-EM article submission agreement, all authors are required to disclose all affiliations, funding sources and financial or management relationships that could be perceived as potential sources of bias. The authors disclosed none.
Figures
References
-
- Andersen LV, Lip GY, Lindholt JS, et al. Upper limb arterial thromboembolism: a systematic review on incidence, risk factors, and prognosis, including a meta-analysis of risk-modifying drugs. J Thromb Haemost. 2013;11(5):836–44. - PubMed
-
- Haimovici H. Cardiogenic embolism of the upper extremity. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 1982;23(3):209–13. - PubMed
-
- Crawford JD, Perrone KH, Jung E, et al. Arterial duplex for diagnosis of peripheral arterial emboli. J Vasc Surg. 2016;64(5):1351–6. - PubMed