Role of Backbone Dynamics in Modulating the Interactions of Disordered Ligands with the TAZ1 Domain of the CREB-Binding Protein
- PMID: 30775911
- PMCID: PMC6414276
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01290
Role of Backbone Dynamics in Modulating the Interactions of Disordered Ligands with the TAZ1 Domain of the CREB-Binding Protein
Abstract
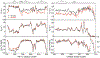
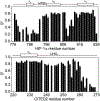
The intrinsically disordered transactivation domains of HIF-1α and CITED2 compete for binding of the TAZ1 domain of the CREB-binding protein by a unidirectional allosteric mechanism involving direct competition for shared binding sites, ternary complex formation, and TAZ1 conformational changes. To gain insight into the mechanism by which CITED2 displaces HIF-1α from TAZ1, we used nuclear magnetic resonance spin relaxation methods to obtain an atomic-level description of the picosecond to nanosecond backbone dynamics that contribute to TAZ1 binding and competition. We show that HIF-1α and CITED2 adopt different dynamics in their complexes with TAZ1, with flexibility observed for HIF-1α in regions that would maintain accessibility for CITED2 to bind to TAZ1 and facilitate subsequent HIF-1α dissociation. In contrast, critical regions of CITED2 adopt a rigid structure in its complex with TAZ1, minimizing the ability of HIF-1α to compete for binding. We also find that TAZ1, previously thought to be a rigid scaffold for binding of disordered protein ligands, displays altered backbone dynamics in its various bound states. TAZ1 is more rigid in its CITED2-bound state than in its free state or in complex with HIF-1α, with increased rigidity observed not only in the CITED2 binding site but also in regions of TAZ1 that undergo conformational changes between the HIF-1α- and CITED2-bound structures. Taken together, these data suggest that backbone dynamics in TAZ1, as well as in the HIF-1α and CITED2 ligands, play a role in modulating the occupancy of TAZ1 and highlight the importance of characterizing both binding partners in molecular interactions.
Figures




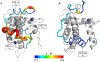
References
-
- van der Lee R, Buljan M, Lang B, Weatheritt RJ, Daughdrill GW, Dunker AK, Fuxreiter M, Gough J, Gsponer J, Jones DT, Kim PM, Kriwacki RW, Oldfield CJ, Pappu RV, Tompa P, Uversky VN, Wright PE, and Babu MM (2014) Classification of intrinsically disordered regions and proteins, Chemical reviews 114, 6589–6631. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sammak S, and Zinzalla G. (2015) Targeting protein-protein interactions (PPIs) of transcription factors: Challenges of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) and regions (IDRs), Progress in biophysics and molecular biology 119, 41–46. - PubMed
-
- Tsafou K, Tiwari PB, Forman-Kay JD, Metallo SJ, and Toretsky JA (2018) Targeting Intrinsically Disordered Transcription Factors: Changing the Paradigm, J Mol Biol 430, 2321–2341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

