Assessment of Screen Exposure in Young Children, 1997 to 2014
- PMID: 30776061
- PMCID: PMC6450267
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.5546
Assessment of Screen Exposure in Young Children, 1997 to 2014
Abstract
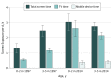
This study evaluates changes in types of screen time exposure among young children before and after the widespread availability of mobile devices.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- American Acemedy of Pediatrics. American Academy of Pediatrics announces new recommendations for children’s media use. https://www.aap.org/en-us/about-the-aap/aap-press-room/Pages/American-Ac.... Published October 21, 2016. Accessed August 9, 2018.
-
- Rideout V. The Common Sense Census: Media Use by Kids Age Zero to Eight. San Francisco, CA: Common Sense Media; 2017.

