Sensitive and immunogen-specific serological detection of Rodentibacter pneumotropicus infections in mice
- PMID: 30777007
- PMCID: PMC6380038
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-019-1417-7
Sensitive and immunogen-specific serological detection of Rodentibacter pneumotropicus infections in mice
Abstract
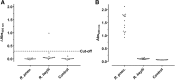
Background: Rodentibacter (R.) pneumotropicus colonizes the respiratory and urogenital tracts of laboratory mice with a reported moderate serological prevalence from 4 to 13%. Thus, regular tests to identify this pathogen in mice are recommended for animal facilities. However, a recent study indicated that current serological assays are partly insensitive, as C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice infected with R. pneumotropicus were incorrectly screened as seronegative.
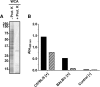
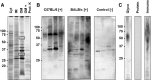
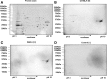
Results: Here, we report a systematic analysis of protein and lipopolysaccharides antigens by immunoblot and ELISA that allowed establishing a sensitive test system able to differentiate between R. pneumotropicus and the closely related species R. heylii. Furthermore, the main immunogen, designated as 'characteristic antigen for Rodentibacter of laboratory origin 1' (CARLO-1), was identified by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis followed by immunoblot and tandem mass spectrometry in a preparation of outer membrane proteins. An indirect ELISA relying on the recombinantly expressed protein provided high sensitivity, specificity, and selectivity. The corresponding carlo1 gene was highly conserved (> 97%) among 21 isolates of R. pneumotropicus and R. heylii.
Conclusion: The newly identified protein CARLO-1 is well suited for the sensitive and specific serological detection of Rodentibacter infections in mice. Indirect differentiation of R. pneumotropicus and R. heylii infections may be possible using an ELISA based on a whole-cell antigen preparation. All four established ELISA systems using a whole-cell preparation, lipopolysaccharides, outer-membrane proteins and protein CARLO-1 as antigen, respectively, outperformed a commercial ELISA in terms of sensitivity.
Keywords: Antigen; CARLO-1; ELISA; FELASA; Health monitoring; Pasteurella pneumotropica; Rodentibacter heylii; Rodentibacter pneumotropicus; Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This animal study was registered and approved under no. TVV 17/15 at the Provincial Head Office Saxony (Germany), Unit 24, Veterinary and Food Inspection (Landesdirektion Sachsen, Referat 24, Veterinärwesen und Lebensmittelüberwachung), which includes approval through the registered committee for animal experiments. This study and handling of mice in general was conducted in strict accordance with the principles outlined in the EU Directive 2010/63/EU and German Animal Protection Law.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
GVG Diagnostics GmbH (Leipzig, Germany) is a provider of diagnostic services for laboratory animals. FF is a part-time employee of GVG Diagnostics.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Adhikary S, Nicklas W, Bisgaard M, Boot R, Kuhnert P, Waberschek T, et al. Rodentibacter gen. Nov. including R. pneumotropicus comb. nov., R. heylii sp. nov., R. myodis sp. nov., R. ratti sp. nov., R. heidelbergensis sp. nov., R. trehalosifermentans sp. nov., R. rarus sp. nov., R. mrazii and two genomospecies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017;67:1793–1806. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001866. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barthold SW, Stephen MG, Percy DH. Mouse. In: Pathology of laboratory rodents and rabbits. 4th ed: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2016. p. 1–118.
-
- Fornefett J, Krause J, Klose K, Fingas F, Hassert R, Benga L, et al. Comparative analysis of humoral immune responses and pathologies of BALB/c and C57BL/6 wildtype mice experimentally infected with a highly virulent Rodentibacter pneumotropicus (Pasteurella pneumotropica) strain. BMC Microbiol. 2018;18(45). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

