Effects of a novel hydrogen sulfide prodrug in a porcine model of acute limb ischemia
- PMID: 30777693
- PMCID: PMC6548642
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvs.2018.08.172
Effects of a novel hydrogen sulfide prodrug in a porcine model of acute limb ischemia
Abstract
Objective: Previous studies have shown that hydrogen sulfide (H2S) exerts potent proangiogenic properties under in vitro conditions and in rodent models. We sought to determine whether a novel H2S prodrug promotes peripheral revascularization in a swine model of acute limb ischemia (ALI).
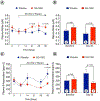
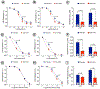
Methods: ALI was induced in 17 female miniswine via intravascular occlusion of the external iliac. At day 7 after ALI induction, miniswine (n = 17) were randomized to received placebo or the H2S prodrug, SG-1002 (800 mg per os twice a day), for 35 days. At day 35 SG-1002 increased circulating levels of H2S (5.0 ± 1.2 μmol/L vs 1.8 ± 0.50 μmol/L; P < .05), sulfane sulfur (10.6 ± 2.3 μmol/L vs 2.6 ± 0.8 μmol/L; P < .05), and nitrite (0.5 ± 0.05 μmol/L vs 0.3 ± 0.03 μmol/L; P < .005) compared with placebo. SG-1002 therapy increased angiographic scoring in ischemic limb vessel number (27.6 ± 1.6 vs 22.2 ± 1.8; P < .05) compared with placebo. Treatment with SG-1002 preserved existing capillaries in ischemic limbs (128.3 ± 18.7 capillaries/mm2 vs 79.0 ± 9.8 capillaries/mm2; P < .05) compared with placebo. Interestingly, treatment with SG-1002 also improved coronary vasorelaxation responses to bradykinin and substance P in miniswine with ALI.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that daily administration of the H2S prodrug, SG-1002, leads to an increase in circulating H2S and nitric oxide signaling and preserves vessel number and density in ischemic limbs. Furthermore, SG-1002 therapy improved endothelial-dependent coronary artery vasorelaxation in the setting of ALI. Our data demonstrate that SG-1002 preserves the vascular architecture in ischemic limbs and exerts vascular protective effects in the coronary vasculature in a model of peripheral vascular disease.
Keywords: Acute limb ischemia; Hydrogen sulfide; Nitric oxide; Peripheral artery disease; Swine.
Copyright © 2018 Society for Vascular Surgery. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Golomb BA, Dang TT, Criqui MH. Peripheral arterial disease: morbidity and mortality implications. Circulation 2006;114: 688–99. - PubMed
-
- Dormandy JA, Rutherford RB. Management of peripheral arterial disease (PAD). TASC Working Group. TransAtlantic Inter-Society Consensus (TASC). J Vasc Surg 2000; 31: S1–S296. - PubMed
-
- Mangiafico RA, Mangiafico M. Medical treatment of critical limb ischemia: current state and future directions. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2011; 9: 658–676. - PubMed
-
- Howell MA, Colgan MP, Seeger RW, Ramsey DE, Sumner DS. Relationship of severity of lower limb peripheral vascular disease to mortality and morbidity: a six-year follow-up study. J Vasc Surg 1989; 9: 691–696. - PubMed
-
- Reinecke H, Unrath M, Freisinger E, Bunzemeier H, Meyborg M, Lüders F, et al. Peripheral arterial disease and critical limb ischemia: Still poor outcomes and lack of guideline adherence." Eur Heart J 2015; 36: 932–938. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

