Hydrogen Sulfide Protects Hyperhomocysteinemia-Induced Renal Damage by Modulation of Caveolin and eNOS Interaction
- PMID: 30778103
- PMCID: PMC6379383
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-38467-6
Hydrogen Sulfide Protects Hyperhomocysteinemia-Induced Renal Damage by Modulation of Caveolin and eNOS Interaction
Abstract
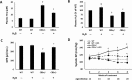
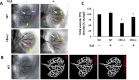
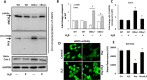
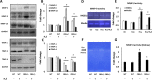
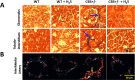
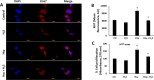
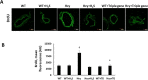
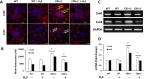
The accumulation of homocysteine (Hcy) during chronic kidney failure (CKD) can exert toxic effects on the glomeruli and tubulo-interstitial region. Among the potential mechanisms, the formation of highly reactive metabolite, Hcy thiolactone, is known to modify proteins by N-homocysteinylation, leading to protein degradation, stress and impaired function. Previous studies documented impaired nitric oxide production and altered caveolin expression in hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy), leading to endothelial dysfunction. The aim of this study was to determine whether Hhcy homocysteinylates endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and alters caveolin-1 expression to decrease nitric oxide bioavailability, causing hypertension and renal dysfunction. We also examined whether hydrogen sulfide (H2S) could dehomocysteinylate eNOS to protect the kidney. WT and Cystathionine β-Synthase deficient (CBS+/-) mice representing HHcy were treated without or with sodium hydrogen sulfide (NaHS), a H2S donor (30 µM), in drinking water for 8 weeks. Hhcy mice (CBS+/-) showed low levels of plasma H2S, elevated systolic blood pressure (SBP) and renal dysfunction. H2S treatment reduced SBP and improved renal function. Hhcy was associated with homocysteinylation of eNOS, reduced enzyme activity and upregulation of caveolin-1 expression. Further, Hhcy increased extracellular matrix (ECM) protein deposition and disruption of gap junction proteins, connexins. H2S treatment reversed the changes above and transfection of triple genes producing H2S (CBS, CSE and 3MST) showed reduction of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. We conclude that during Hhcy, homocysteinylation of eNOS and disruption of caveolin-mediated regulation leads to ECM remodeling and hypertension, and H2S treatment attenuates renovascular damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increased endogenous H2S generation by CBS, CSE, and 3MST gene therapy improves ex vivo renovascular relaxation in hyperhomocysteinemia.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Jul 1;303(1):C41-51. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00398.2011. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22517358 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperhomocysteinemia potentiates diabetes-impaired EDHF-induced vascular relaxation: Role of insufficient hydrogen sulfide.Redox Biol. 2018 Jun;16:215-225. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.02.006. Epub 2018 Feb 14. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 29524844 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates hyperhomocysteinemia-associated chronic renal failure.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009 Aug;297(2):F410-9. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00145.2009. Epub 2009 May 27. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19474193 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of skeletal muscle homeostasis by hydrogen sulfide during hyperhomocysteinemia-mediated oxidative/ER stress condition 1.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019 Jun;97(6):441-456. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2018-0501. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30422673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting hydrogen sulfide as a promising therapeutic strategy for atherosclerosis.Int J Cardiol. 2014 Mar 15;172(2):313-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.01.068. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Int J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24491853 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted delivery of celastrol to glomerular endothelium and podocytes for chronic kidney disease treatment.Nano Res. 2022;15(4):3556-3568. doi: 10.1007/s12274-021-3894-x. Epub 2021 Dec 12. Nano Res. 2022. PMID: 34925707 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Hydrogen Sulfide Donors in Common Kidney Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 19;11:564281. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.564281. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33364941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homocysteine induces ferroptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells via β-catenin/GPX4 signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 4;15(1):23953. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09221-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40615532 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Caveolin-1 in Diabetes and Its Complications.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jan 27;2020:9761539. doi: 10.1155/2020/9761539. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32082483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pathophysiology of H2S in Renal Glomerular Diseases.Biomolecules. 2022 Jan 26;12(2):207. doi: 10.3390/biom12020207. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204708 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

