Protein-coding variants implicate novel genes related to lipid homeostasis contributing to body-fat distribution
- PMID: 30778226
- PMCID: PMC6560635
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0334-2
Protein-coding variants implicate novel genes related to lipid homeostasis contributing to body-fat distribution
Abstract
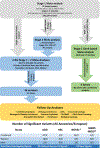
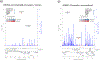
Body-fat distribution is a risk factor for adverse cardiovascular health consequences. We analyzed the association of body-fat distribution, assessed by waist-to-hip ratio adjusted for body mass index, with 228,985 predicted coding and splice site variants available on exome arrays in up to 344,369 individuals from five major ancestries (discovery) and 132,177 European-ancestry individuals (validation). We identified 15 common (minor allele frequency, MAF ≥5%) and nine low-frequency or rare (MAF <5%) coding novel variants. Pathway/gene set enrichment analyses identified lipid particle, adiponectin, abnormal white adipose tissue physiology and bone development and morphology as important contributors to fat distribution, while cross-trait associations highlight cardiometabolic traits. In functional follow-up analyses, specifically in Drosophila RNAi-knockdowns, we observed a significant increase in the total body triglyceride levels for two genes (DNAH10 and PLXND1). We implicate novel genes in fat distribution, stressing the importance of interrogating low-frequency and protein-coding variants.
Figures

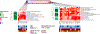
Similar articles
-
Association of Genetic Variants Related to Gluteofemoral vs Abdominal Fat Distribution With Type 2 Diabetes, Coronary Disease, and Cardiovascular Risk Factors.JAMA. 2018 Dec 25;320(24):2553-2563. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.19329. JAMA. 2018. PMID: 30575882 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for body fat distribution in 694 649 individuals of European ancestry.Hum Mol Genet. 2019 Jan 1;28(1):166-174. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy327. Hum Mol Genet. 2019. PMID: 30239722 Free PMC article.
-
Rare and Coding Region Genetic Variants Associated With Risk of Ischemic Stroke: The NHLBI Exome Sequence Project.JAMA Neurol. 2015 Jul;72(7):781-8. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.0582. JAMA Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25961151 Free PMC article.
-
The genetics of adiposity.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2018 Jun;50:86-95. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2018.02.009. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2018. PMID: 29529423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive identification of pleiotropic loci for body fat distribution using the NHGRI-EBI Catalog of published genome-wide association studies.Obes Rev. 2019 Mar;20(3):385-406. doi: 10.1111/obr.12806. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Obes Rev. 2019. PMID: 30565845 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetics of sexually dimorphic adipose distribution in humans.Nat Genet. 2023 Mar;55(3):461-470. doi: 10.1038/s41588-023-01306-0. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Nat Genet. 2023. PMID: 36797366 Free PMC article.
-
Rare variant associations with birth weight identify genes involved in adipose tissue regulation, placental function and insulin-like growth factor signalling.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 3:2024.04.03.24305248. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.03.24305248. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 14;16(1):648. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55761-2. PMID: 38633783 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Systems genetic analysis of binge-like eating in a C57BL/6J x DBA/2J-F2 cross.Genes Brain Behav. 2021 May 12:e12751. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12751. Online ahead of print. Genes Brain Behav. 2021. PMID: 33978997 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Basis of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes in Africans: Impact on Precision Medicine.Curr Diab Rep. 2019 Sep 14;19(10):105. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1215-5. Curr Diab Rep. 2019. PMID: 31520154 Review.
-
Targeted sequencing analysis of the adiponectin gene identifies variants associated with obstructive sleep apnoea in Chinese Han population.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Apr;98(16):e15219. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015219. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31008949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pischon T et al. General and abdominal adiposity and risk of death in Europe. N Engl J Med 359, 2105–20 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC & Hu FB Comparison of abdominal adiposity and overall obesity in predicting risk of type 2 diabetes among men. Am J Clin Nutr 81, 555–63 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Canoy D Distribution of body fat and risk of coronary heart disease in men and women. Curr Opin Cardiol 23, 591–8 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Snijder MB et al. Associations of hip and thigh circumferences independent of waist circumference with the incidence of type 2 diabetes: the Hoorn Study. Am J Clin Nutr 77, 1192–7 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S et al. Obesity and the risk of myocardial infarction in 27,000 participants from 52 countries: a case-control study. Lancet 366, 1640–9 (2005). - PubMed
REFERENCES – ONLINE METHODS ONLY
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K99 HL130580/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/18/13/33946/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HG008983/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK101855/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_EX_MR/M009203/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/S003746/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 16563/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P30 DK056336/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007055/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL121422/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- FS/12/82/29736/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_00007/10/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 HG007417/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- G9521010/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK106621/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RG/13/13/30194/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- U01 HG007416/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM126479/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA040177/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 16565/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- RG/08/014/24067/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 212945/Z/18/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- KL2 TR001109/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL130580/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L01632X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK110113/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079626/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK107786/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_14089/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M009203/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK075787/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L01341X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL119443/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD043483/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MR/R023484/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK107904/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089256/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RG/14/5/30893/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HD057194/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

