Single-dose CRISPR-Cas9 therapy extends lifespan of mice with Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome
- PMID: 30778240
- PMCID: PMC6541418
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-019-0343-4
Single-dose CRISPR-Cas9 therapy extends lifespan of mice with Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome
Abstract
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) is a rare lethal genetic disorder characterized by symptoms reminiscent of accelerated aging. The major underlying genetic cause is a substitution mutation in the gene coding for lamin A, causing the production of a toxic isoform called progerin. Here we show that reduction of lamin A/progerin by a single-dose systemic administration of adeno-associated virus-delivered CRISPR-Cas9 components suppresses HGPS in a mouse model.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The Authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

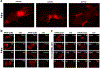
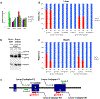
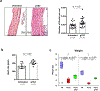
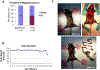


References
-
- Broers JL, Ramaekers FC, Bonne G, Yaou RB & Hutchison CJ Nuclear lamins: laminopathies and their role in premature ageing. Physiol Rev 86, 967–1008 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Ahmed MS, Ikram S, Bibi N & Mir A Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome: A Premature Aging Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 55, 4417–4427 (2018) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

