Neuroimmune and epigenetic involvement in adolescent binge ethanol-induced loss of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons: Restoration with voluntary exercise
- PMID: 30779268
- PMCID: PMC6698434
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.12731
Neuroimmune and epigenetic involvement in adolescent binge ethanol-induced loss of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons: Restoration with voluntary exercise
Abstract
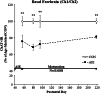
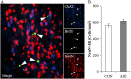
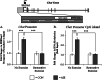
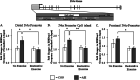
Binge drinking and alcohol abuse are common during adolescence and cause lasting pathology. Preclinical rodent studies using the adolescent intermittent ethanol (AIE; 5.0 g/kg, i.g., 2-day on/2-day off from postnatal day [P]25 to P55) model of human adolescent binge drinking report decreased basal forebrain cholinergic (ie, ChAT+) neurons that persist into adulthood (ie, P56-P220). Recent studies link AIE-induced neuroimmune activation to cholinergic pathology, but the underlying molecular mechanisms contributing to the persistent loss of basal forebrain ChAT+ neurons are unknown. We report here that the AIE-induced loss of cholinergic neuron markers (ie, ChAT, TrkA, and p75NTR ), cholinergic neuron shrinkage, and increased expression of the neuroimmune marker pNF-κB p65 are restored by exercise exposure from P56 to P95 after AIE. Our data reveal that persistently reduced expression of cholinergic neuron markers following AIE is because of the loss of the cholinergic neuron phenotype most likely through an epigenetic mechanism involving DNA methylation and histone 3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2). Adolescent intermittent ethanol caused a persistent increase in adult H3K9me2 and DNA methylation at promoter regions of Chat and H3K9me2 of Trka, which was restored by wheel running. Exercise also restored the AIE-induced reversal learning deficits on the Morris water maze. Together, these data suggest that AIE-induced adult neuroimmune signaling and cognitive deficits are linked to suppression of Chat and Trka gene expression through epigenetic mechanisms that can be restored by exercise. Exercise restoration of the persistent AIE-induced phenotypic loss of cholinergic neurons via epigenetic modifications is novel mechanism of neuroplasticity.
Keywords: adolescence; alcohol; binge drinking; choline acetyltransferase; methylation; reversal learning.
© 2019 The Authors Addiction Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Epigenetic regulation of microglia and neurons by proinflammatory signaling following adolescent intermittent ethanol (AIE) exposure and in human AUD.Adv Drug Alcohol Res. 2024 Mar 8;4:12094. doi: 10.3389/adar.2024.12094. eCollection 2024. Adv Drug Alcohol Res. 2024. PMID: 38524847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HMGB1 neuroimmune signaling and REST-G9a gene repression contribute to ethanol-induced reversible suppression of the cholinergic neuron phenotype.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Dec;28(12):5159-5172. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02160-6. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37402853 Free PMC article.
-
Adolescent binge ethanol-induced loss of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons and neuroimmune activation are prevented by exercise and indomethacin.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 8;13(10):e0204500. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204500. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30296276 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons Following Adolescent Binge Ethanol Exposure: Recovery With the Cholinesterase Inhibitor Galantamine.Front Behav Neurosci. 2021 Feb 26;15:652494. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.652494. eCollection 2021. Front Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33716687 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Persistent Changes in Neuroimmune and Epigenetic Signaling in Adolescent Drinking to Treat Alcohol Use Disorder in Adulthood.Pharmacol Rev. 2023 Mar;75(2):380-396. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.122.000710. Epub 2022 Dec 12. Pharmacol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36781218 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adolescent alcohol exposure disrupts episodic-like memory by impairing dopamine synapses in the mouse prelimbic cortex.Neuropharmacology. 2025 Mar 1;265:110255. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.110255. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Neuropharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39643240
-
Ethanol changes Nestin-promoter induced neural stem cells to disturb newborn dendritic spine remodeling in the hippocampus of mice.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Feb;19(2):416-424. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.379051. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37488906 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of microglia and neurons by proinflammatory signaling following adolescent intermittent ethanol (AIE) exposure and in human AUD.Adv Drug Alcohol Res. 2024 Mar 8;4:12094. doi: 10.3389/adar.2024.12094. eCollection 2024. Adv Drug Alcohol Res. 2024. PMID: 38524847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HMGB1 neuroimmune signaling and REST-G9a gene repression contribute to ethanol-induced reversible suppression of the cholinergic neuron phenotype.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Dec;28(12):5159-5172. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02160-6. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37402853 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol and stress exposure across the lifespan are key risk factors for Alzheimer's Disease and cognitive decline.Neurobiol Stress. 2024 Jan 4;29:100605. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2024.100605. eCollection 2024 Mar. Neurobiol Stress. 2024. PMID: 38268931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spear LP. The Behavioral Neuroscience of Adolescence. 1st edition ed. New York: W. W. Norton & Co Inc; 2009.
-
- Blake MG, Boccia MM (2017) Basal Forebrain Cholinergic System and Memory. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. - PubMed
-
- Mesulam MM, Mufson EJ, Wainer BH, Levey AI. Central cholinergic pathways in the rat: an overview based on an alternative nomenclature (Ch1‐Ch6). Neuroscience. 1983;10(4):1185‐1201. - PubMed
-
- Johnston LD, O'Malley PM, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE. Monitoring the Future National Results on Drug Use: 2012 Overview, Key Findings on Adolescent Drug Use. Ann Arbor: Institute for Social Research, The University of Michigan; 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

