Effectiveness of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines against invasive pneumococcal disease among children under five years of age in Africa: A systematic review
- PMID: 30779801
- PMCID: PMC6380553
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212295
Effectiveness of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines against invasive pneumococcal disease among children under five years of age in Africa: A systematic review
Abstract
Background: Despite the widespread implementation of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, Streptococcus pneumoniae remains the leading cause of severe pneumonia associated with mortality among children less than 5 years of age worldwide, with the highest mortality rates recorded in Africa and Asia. However, information on the effectiveness and prevalence of vaccine serotypes post-roll out remains scarce in most African countries. Hence, this systematic review aimed to describe what is known about the decline of childhood invasive pneumococcal disease post-introduction of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in Africa.
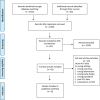
Methods: This systematic review included articles published between 2009 and 2018 on the implementation of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in Africa. We searched PubMed, Scopus and African Index Medicus for articles in English. Studies on implementation programmes of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine 10/13, with before and after data from different African countries, were considered eligible. The review followed the procedures published in PROSPERO (ID = CRD42016049192).
Results: In total, 2,280 studies were identified through electronic database research, and only 8 studies were eligible for inclusion in the final analysis. Approximately half (n = 3) of these studies were from South Africa. The overall decline in invasive pneumococcal disease ranged from 31.7 to 80.1%. Invasive pneumococcal diseases caused by vaccine serotypes declined significantly, the decline ranged from 35.0 to 92.0%. A much higher decline (55.0-89.0%) was found in children below 24 months of age. Of all vaccine serotypes, the relative proportions of serotypes 1, 5 and 19A doubled following vaccine roll out.
Interpretation: Following the introduction of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, a significant decline was observed in invasive pneumococcal disease caused by vaccine serotypes. However, data on the effectiveness in this region remain scarce, meriting continued surveillance to assess the effectiveness of pneumococcal vaccination to improve protection against invasive pneumococcal disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exist.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Pneumococcal vaccines WHO position paper—2012. Relev Epidemiol Hebd. 2012;87: 129–44. - PubMed
-
- Chappuy H, Keitel K, Gehri M, Tabin R, Robitaille L, Raymond F, et al. Nasopharyngeal carriage of individual Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes during pediatric radiologically confirmed community acquired pneumonia following PCV7 introduction in Switzerland. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13: 357 10.1186/1471-2334-13-357 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rudan I, O’Brien KL, Nair H, Liu L, Theodoratou E, Qazi S, et al. Epidemiology and etiology of childhood pneumonia in 2010: estimates of incidence, severe morbidity, mortality, underlying risk factors and causative pathogens for 192 countries. J Glob Health. 2013;3: 010401 10.7189/jogh.03.010401 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

