A New Method for Simultaneous Determination of Phenolic Acids, Alkaloids and Limonoids in Phellodendri Amurensis Cortex
- PMID: 30781392
- PMCID: PMC6413186
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24040709
A New Method for Simultaneous Determination of Phenolic Acids, Alkaloids and Limonoids in Phellodendri Amurensis Cortex
Abstract
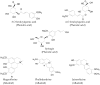
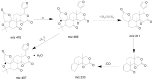
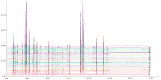
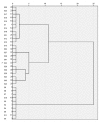
Phellodendri Amurensis Cortex (PAC) is a well-known herbal medicine in China with complex components, but the previous research has mostly focused on its alkaloids analysis. For the first time, a simpler and more efficient method was proposed in this paper to simultaneously determine the content of three different kinds of compounds-phenolic acids, alkaloids and limonoids-in PAC. The phenolic acids included 3-O-feruloylquinic acid, 4-O-feruloylquinic acid and syringin. The alkaloids include magnoflorine, phellodendrine, jatrorrhizine, palmatine and berberine, while the limonoids include obaculactone and obacunone. An approach combining multi-wavelength and HPLC-DAD was used in this study due to the great difference in maximum absorption wavelength of the various components. Four wavelengths at 215, 275, 280 and 310 nm, respectively, were chosen for monitoring. It has been indicated through appropriate tests that this approach is of high accuracy, good repeatability and stability and provides a scientific basis for the quality assessment of PAC and associated derivatives. In addition, the chromatographic fingerprints method combined with multivariate statistical analysis chosen in this study was proved to be effective and reasonable for an accurate classification of 33 batches of samples collected from different locations.
Keywords: alkaloids; limonoids; multi-wavelength; phellodendri amurensis cortex; phenolic acids; quality evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no financial or personal relationships with people or organizations that could inappropriately influence our work.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Fingerprinting and simultaneous determination of alkaloids and limonins in Phellodendri amurensis cortex from different locations by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection.J Chromatogr Sci. 2015 Jan;53(1):161-6. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bmu034. Epub 2014 May 28. J Chromatogr Sci. 2015. PMID: 24872523
-
[Simultaneous determination of jatrorrhizine, palmatine, berberine, and obacunone in Phellodendri Amurensis Cortex by RP-HPLC].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010 Aug;35(16):2061-4. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21046728 Chinese.
-
[Determination of obacunone and obaculactone in different processing products of Phellodendri amurensis cortex].Zhong Yao Cai. 2013 Feb;36(2):205-8. Zhong Yao Cai. 2013. PMID: 23901643 Chinese.
-
Phellodendri Cortex: A Phytochemical, Pharmacological, and Pharmacokinetic Review.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Apr 1;2019:7621929. doi: 10.1155/2019/7621929. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31057654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Dictamni Cortex: a review].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Jul;47(14):3723-3737. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220317.201. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35850829 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of Traditional Tibetan Medicine Grubthobrildkr Alleviated Gastric Ulcer Induced by Acute Systemic Hypoxia in Rats.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Apr 5;2022:4803956. doi: 10.1155/2022/4803956. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35425842 Free PMC article.
-
A new method for simultaneous determination of 14 phenolic acids in agricultural soils by multiwavelength HPLC-PDA analysis.RSC Adv. 2022 May 18;12(23):14939-14944. doi: 10.1039/d1ra09433e. eCollection 2022 May 12. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35702192 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Importance of Phellodendrine in Traditional and Modern Medicines: An Update on Therapeutic Potential in Medicine.Curr Drug Res Rev. 2024;16(2):209-218. doi: 10.2174/2589977515666230721153904. Curr Drug Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 37488762 Review.
-
Based on Proteomics Data Revealing the Potential of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Treating Irritable Bowel Syndrome.Mediators Inflamm. 2025 Jul 23;2025:7748351. doi: 10.1155/mi/7748351. eCollection 2025. Mediators Inflamm. 2025. PMID: 40741600 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Chemistry and Bioactivity of Magnoflorine and Magnoflorine-Containing Extracts.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 16;21(4):1330. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041330. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32079131 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The Pharmacopoeia Commission of the People’s Republic of China . The Pharmacopoeia of PRC: Part I. 1st ed. China Medical Science Press; Beijing, China: 2015.
-
- Yan H., Sun X., Sun S., Wang S., Zhang J., Wang R., An P., Yang F., Kang W. Anti-ultraviolet radiation effects of Coptis chinensis and Phellodendron amurense glycans by immunomodulating and inhibiting oxidative injury. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011;48:720–725. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2011.02.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xian Y.F., Lin Z.X., Ip S.P., Su Z.R., Chen J.N., Lai X.P. Comparison the neuropreotective effect of Cortex Phellodendri chinensis and Cortex Phellodendri amurensis against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Phytomedicine. 2013;20:187–193. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2012.09.028. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

