Sub-lethal Doses of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers, in Vitro, Promote Oxidative Stress and Modulate Molecular Markers Related to Cell Cycle, Antioxidant Balance and Cellular Energy Management
- PMID: 30781636
- PMCID: PMC6406823
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16040588
Sub-lethal Doses of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers, in Vitro, Promote Oxidative Stress and Modulate Molecular Markers Related to Cell Cycle, Antioxidant Balance and Cellular Energy Management
Abstract
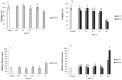
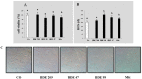
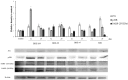
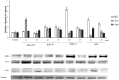
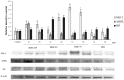
In the present study, we evaluated the effects of different concentrations of the polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) BDE-209, BDE-47 and BDE-99, on the vitality and oxidative stress of a HS-68 human cell culture exposed to the compounds for three days. The results showed that for this exposure time, only the highest concentrations produced a significant vitality reduction and oxidative stress induction (p < 0.05), measured as reactive oxygen species (ROS). Subsequently, in order to verify the effects of sub-lethal doses, cells were exposed for a longer time and data collected, after 12 and 20 days, to study ROS production and some molecular markers related to cell cycle and stress (p53, pRB, PARP, c-Jun and c-Fos), antioxidant status and proliferation (ERK, c-Jun and c-Fos), energy balance (NRF2, AMPK, HIF). Most of the biomarkers were influenced by the treatments, indicating that sub-lethal doses of PBDEs, for longer time, can enhance the production of ROS, altering the energetic metabolism, cell cycle and antioxidant balance, determining possible negative effects on the cell proliferation equilibrium.
Keywords: PBDEs; biomarkers; metabolism; oxidative stress; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sub-lethal doses of polybrominated diphenyl ethers affect some biomarkers involved in energy balance and cell cycle, via oxidative stress in the marine fish cell line SAF-1.Aquat Toxicol. 2019 May;210:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.02.014. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Aquat Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30797971
-
Oxidative Stress, Induced by Sub-Lethal Doses of BDE 209, Promotes Energy Management and Cell Cycle Modulation in the Marine Fish Cell Line SAF-1.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Feb 6;16(3):474. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16030474. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30736298 Free PMC article.
-
Carbamazepine, cadmium chloride and polybrominated diphenyl ether-47, synergistically modulate the expression of antioxidants and cell cycle biomarkers, in the marine fish cell line SAF-1.Mar Environ Res. 2020 Feb;154:104844. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2019.104844. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Mar Environ Res. 2020. PMID: 31784109
-
Exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs): changes in thyroid, vitamin A, glutathione homeostasis, and oxidative stress in American kestrels (Falco sparverius).Toxicol Sci. 2005 Dec;88(2):375-83. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfi295. Epub 2005 Aug 24. Toxicol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16120752
-
[A novel class of environmental contaminants: hydroxylated polybrominated diphenyl ethers (OH-PBDEs)].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2011 Jul;32(7):2169-76. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2011. PMID: 21922848 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Effects of Mixtures of Emerging Pollutants and Drugs on Modulation of Biomarkers Related to Toxicity, Oxidative Stress, and Cancer.Metabolites. 2024 Oct 17;14(10):559. doi: 10.3390/metabo14100559. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39452940 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Male Reproductive Toxicity of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 17;23(22):14229. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214229. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDE-47, -99, -209 and Their Ternary Mixture Disrupt Glucose and Lipid Metabolism of Hepg2 Cells at Dietary Relevant Concentrations: Mechanistic Insight through Integrated Transcriptomics and Proteomics Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 21;23(22):14465. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214465. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430946 Free PMC article.
-
Microplastics as Emerging Contaminants and Human Health: Exploring Functional Nutrition in Gastric-Colon-Brain Axis Cancer.Toxics. 2025 May 26;13(6):438. doi: 10.3390/toxics13060438. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 40559911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell transcriptomics unveiled that early life BDE-99 exposure reprogrammed the gut-liver axis to promote a proinflammatory metabolic signature in male mice at late adulthood.Toxicol Sci. 2024 Jun 26;200(1):114-136. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfae047. Toxicol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38648751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eljarrat E., Barceló D. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry. Part J. PAHs Relat. Compd. 2011 doi: 10.1016/0143-1471(82)90111-8. - DOI
-
- De Boer J., Allchin C., Law R., Zegers B., Boon J.P. Method for the analysis of polybrominated diphenylethers in sediments and biota. Trends Anal. Chem. 2001;20:591–599. doi: 10.1016/S0165-9936(01)00097-8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

