The Effectiveness of Vitamin E Treatment in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 30781638
- PMCID: PMC6412423
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20040879
The Effectiveness of Vitamin E Treatment in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
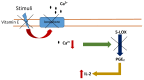
Vitamin E was proposed as treatment for Alzheimer's disease many years ago. However, the effectiveness of the drug is not clear. Vitamin E is an antioxidant and neuroprotector and it has anti-inflammatory and hypocholesterolemic properties, driving to its importance for brain health. Moreover, the levels of vitamin E in Alzheimer's disease patients are lower than in non-demented controls. Thus, vitamin E could be a good candidate to have beneficial effects against Alzheimer's. However, evidence is consistent with a limited effectiveness of vitamin E in slowing progression of dementia; the information is mixed and inconclusive. The question is why does vitamin E fail to treat Alzheimer's disease? In this paper we review the studies with and without positive results in Alzheimer's disease and we discuss the reasons why vitamin E as treatment sometimes has positive results on cognition but at others, it does not.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; antioxidants; brain health; non-respondents; respondents to vitamin E.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Vitamin E in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease: Evidence from Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 23;18(12):2504. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122504. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29168797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin E and Alzheimer disease: the basis for additional clinical trials.Am J Clin Nutr. 2000 Feb;71(2):630S-636S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/71.2.630s. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000. PMID: 10681271 Review.
-
[Vitamin E and Alzheimer's Disease].Brain Nerve. 2015 Dec;67(12):1509-13. doi: 10.11477/mf.1416200330. Brain Nerve. 2015. PMID: 26618765 Review. Japanese.
-
Effects of vitamin E on cognitive performance during ageing and in Alzheimer's disease.Nutrients. 2014 Nov 28;6(12):5453-72. doi: 10.3390/nu6125453. Nutrients. 2014. PMID: 25460513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacologic approaches to cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease.J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59 Suppl 9:22-7. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998. PMID: 9720483 Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential Role of Nutrition in Lung Cancer Establishment and Progression.Life (Basel). 2022 Feb 12;12(2):270. doi: 10.3390/life12020270. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35207557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress and Tauopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 22;20(8):1959. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081959. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31013607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutraceuticals and Their Contribution to Preventing Noncommunicable Diseases.Foods. 2023 Aug 30;12(17):3262. doi: 10.3390/foods12173262. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37685194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical Composition, Antioxidant, and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities of Artemisia schmidtiana Maxim. Essential Oil.Biomolecules. 2025 May 19;15(5):736. doi: 10.3390/biom15050736. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40427629 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Water-Insoluble Vehicle Comprising Natural Cyclodextrin-Vitamin E Complex.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Mar 20;10(3):490. doi: 10.3390/antiox10030490. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33804761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Masters C.L., Multhaup G., Simms G., Pottgiesser J., Martins R.N., Beyreuther K. Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer’s disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J. 1985;4:2757–2763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04000.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

