Ex Vivo Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells for Therapeutic Purposes: Lessons from Development and the Niche
- PMID: 30781676
- PMCID: PMC6407064
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8020169
Ex Vivo Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells for Therapeutic Purposes: Lessons from Development and the Niche
Abstract
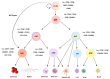
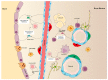
Expansion of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) for therapeutic purposes has been a "holy grail" in the field for many years. Ex vivo expansion of HSCs can help to overcome material shortage for transplantation purposes and genetic modification protocols. In this review, we summarize improved understanding in blood development, the effect of niche and conservative signaling pathways on HSCs in mice and humans, and also advances in ex vivo culturing protocols of human HSCs with cytokines or small molecule compounds. Different expansion protocols have been tested in clinical trials. However, an optimal condition for ex vivo expansion of human HSCs still has not been found yet. Translating and implementing new findings from basic research (for instance by using genetic modification of human HSCs) into clinical protocols is crucial to improve ex vivo expansion and eventually boost stem cell gene therapy.
Keywords: clinics; ex vivo expansion; gene therapy; hematopoietic stem cell; transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Different Cytokine Conditions Reveals Resveratrol as a New Molecule for Ex Vivo Cultivation of Cord Blood-Derived Hematopoietic Stem Cells.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015 Sep;4(9):1064-72. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2014-0284. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26160960 Free PMC article.
-
Ex vivo expansion of hematopoietic stem cells.Sci China Life Sci. 2015 Sep;58(9):839-53. doi: 10.1007/s11427-015-4895-3. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Sci China Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26246379 Review.
-
HSC Niche Biology and HSC Expansion Ex Vivo.Trends Mol Med. 2017 Sep;23(9):799-819. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2017.07.003. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Trends Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28801069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hematopoietic stem cells: self-renewal and expansion.Curr Opin Hematol. 2019 Jul;26(4):258-265. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000506. Curr Opin Hematol. 2019. PMID: 31170110 Review.
-
Advances in hematopoietic stem cells ex vivo expansion associated with bone marrow niche.Ann Hematol. 2024 Dec;103(12):5035-5057. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05773-1. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38684510 Review.
Cited by
-
Pluripotent stem cell-based gene therapy approach: human de novo synthesized chromosomes.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Feb;78(4):1207-1220. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03653-1. Epub 2020 Oct 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33011821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL3 Has a Detrimental Effect on Hematopoietic Stem Cell Self-Renewal in Transplantation Settings.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 22;23(21):12736. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112736. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361533 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of osteoclast differentiation protocols from human induced pluripotent stem cells of different tissue origins.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Nov 7;14(1):319. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03547-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37936199 Free PMC article.
-
Levistilide A Promotes Expansion of Human Umbilical Cord Blood Hematopoietic Stem Cells by Enhancing Antioxidant Activity.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 17;13:806837. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.806837. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35250558 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing Blood Stem Cell Transplants Through Cellular Engineering.Blood Cell Ther. 2022 Jan 14;5(1):1-15. doi: 10.31547/bct-2021-008. eCollection 2022 Feb 25. Blood Cell Ther. 2022. PMID: 36714264 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

