Cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 30782145
- PMCID: PMC6381635
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-019-1268-y
Cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
Background: Cathelicidins are a major group of natural antimicrobial peptides which play essential roles in regulating host defense and immunity. In addition to the antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activities, recent studies have reported the involvement of cathelicidins in cardiovascular diseases by regulating inflammatory response and microvascular dysfunction. However, the role of cathelicidins in myocardial apoptosis upon cardiac ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury remains largely unknown.
Methods: CRAMP (cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide) levels were measured in the heart and serum from I/R mice and in neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes treated with oxygen glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGDR). Human serum cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (LL-37) levels were measured in myocardial infarction (MI) patients. The role of CRAMP in myocardial apoptosis upon I/R injury was investigated in mice injected with the CRAMP peptide and in CRAMP knockout (KO) mice, as well as in OGDR-treated cardiomyocytes.
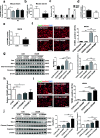
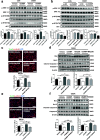
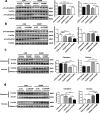
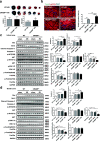
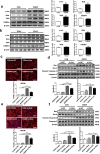
Results: We observed reduced CRAMP level in both heart and serum samples from I/R mice and in OGDR-treated cardiomyocytes, as well as reduced LL-37 level in MI patients. Knockdown of CRAMP enhanced cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and CRAMP KO mice displayed increased infarct size and myocardial apoptosis. In contrast, the CRAMP peptide reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and I/R injury. The CRAMP peptide inhibited cardiomyocyte apoptosis by activation of Akt and ERK1/2 and phosphorylation and nuclear export of FoxO3a. c-Jun was identified as a negative regulator of the CRAMP gene. Moreover, lower level of serum LL-37/neutrophil ratio was associated with readmission and/or death in MI patients during 1-year follow-up.
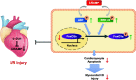
Conclusions: CRAMP protects against cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac I/R injury via activation of Akt and ERK and phosphorylation and nuclear export of FoxO3a. Increasing LL-37 might be a novel therapy for cardiac ischemic injury.
Keywords: Apoptosis; CRAMP; Cardiomyocyte; Cathelicidin; Ischemia/reperfusion injury; LL-37.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All human investigations conformed to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki and were approved by the institutional review committees of Tongji Hospital (2014-002). The MI patients and healthy controls were recruited with a written informed consent at Tongji Hospital (Shanghai, China) from July 2015 to June 2017. All procedures with animals were in accordance with the guidelines on the use and care of laboratory animals for biomedical research published by National Institutes of Health (No. 85-23, revised 1996), and the experimental protocol was reviewed and approved by the ethical committees of Shanghai University (Shanghai, China).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cathelicidin aggravates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via activating TLR4 signaling and P2X7R/NLRP3 inflammasome.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020 Feb;139:75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.12.011. Epub 2020 Jan 23. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 31982429
-
Cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide protects against ischaemia reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Jun;177(12):2726-2742. doi: 10.1111/bph.14998. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31976546 Free PMC article.
-
Cathelicidins Target HSP60 To Restrict CVB3 Transmission via Disrupting the Exosome and Reducing Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis.J Virol. 2023 Mar 30;97(3):e0143322. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01433-22. Epub 2023 Mar 14. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 36916989 Free PMC article.
-
The Critical Role of the Antimicrobial Peptide LL-37/ CRAMP in Protection of Colon Microbiota Balance, Mucosal Homeostasis, Anti-Inflammatory Responses, and Resistance to Carcinogenesis.Crit Rev Immunol. 2019;39(2):83-92. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2019030225. Crit Rev Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31679249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cathelicidins: peptides with antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, angiogenic, anticancer and procancer activities.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2013 Sep;14(6):504-14. doi: 10.2174/13892037113149990067. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2013. PMID: 23968350 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of key genes associated with acute myocardial infarction using WGCNA and two-sample mendelian randomization study.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 18;19(7):e0305532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305532. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39024234 Free PMC article.
-
Dapagliflozin Mediates Plin5/PPARα Signaling Axis to Attenuate Cardiac Hypertrophy.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 23;12:730623. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.730623. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34630108 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-microbial peptide LL-37/CRAMP levels are associated with acute heart failure and can attenuate cardiac dysfunction in multiple preclinical models of heart failure.Theranostics. 2020 May 15;10(14):6167-6181. doi: 10.7150/thno.46225. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32483446 Free PMC article.
-
Gene therapy for cardiovascular diseases in China: basic research.Gene Ther. 2020 Aug;27(7-8):360-369. doi: 10.1038/s41434-020-0148-6. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Gene Ther. 2020. PMID: 32341485 Review.
-
Exercise-induced peptide TAG-23 protects cardiomyocytes from reperfusion injury through regulating PKG-cCbl interaction.Basic Res Cardiol. 2021 Jun 25;116(1):41. doi: 10.1007/s00395-021-00878-4. Basic Res Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 34173041 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

