Complex karyotype AML displays G2/M signature and hypersensitivity to PLK1 inhibition
- PMID: 30782614
- PMCID: PMC6391664
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018028480
Complex karyotype AML displays G2/M signature and hypersensitivity to PLK1 inhibition
Abstract
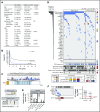
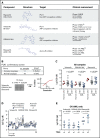
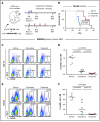
Patients diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia with complex karyotype (CK AML) have an adverse prognosis using current therapies, especially when accompanied by TP53 alterations. We hereby report the RNA-sequencing analysis of the 68 CK AML samples included in the Leucegene 415 patient cohort. We confirm the frequent occurrence of TP53 alterations in this subgroup and further characterize the allele expression profile and transcript alterations of this gene. We also document that the RAS pathway (N/KRAS, NF1, PTPN11, BRAF) is frequently altered in this disease. Targeted chemical interrogation of genetically characterized primary CK AML samples identifies polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) inhibitors as the most selective agents for this disease subgroup. TP53 status did not alter sensitivity to PLK1 inhibitors. Interestingly, CK AML specimens display a G2/M transcriptomic signature that includes higher expression levels of PLK1 and correlates with PLK1 inhibition sensitivity. Together, our results highlight vulnerability in CK AML. In line with these in vitro data, volasertib shows a strong anti-AML activity in xenotransplantation mouse models of human adverse AML. Considering that PLK1 inhibitors are currently being investigated clinically in AML and myelodysplastic syndromes, our results provide a new rationale for PLK1-directed therapy in patients with adverse cytogenetic AML.
© 2019 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. , eds. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, Revised 4th edition Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2017
-
- Grimwade D, Hills RK, Moorman AV, et al. ; National Cancer Research Institute Adult Leukaemia Working Group. Refinement of cytogenetic classification in acute myeloid leukemia: determination of prognostic significance of rare recurring chromosomal abnormalities among 5876 younger adult patients treated in the United Kingdom Medical Research Council trials. Blood. 2010;116(3):354-365. - PubMed
-
- Rücker FG, Schlenk RF, Bullinger L, et al. . TP53 alterations in acute myeloid leukemia with complex karyotype correlate with specific copy number alterations, monosomal karyotype, and dismal outcome. Blood. 2012;119(9):2114-2121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

