High-throughput, Efficient, and Unbiased Capture of Small RNAs from Low-input Samples for Sequencing
- PMID: 30783180
- PMCID: PMC6381177
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-38458-7
High-throughput, Efficient, and Unbiased Capture of Small RNAs from Low-input Samples for Sequencing
Abstract
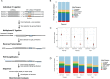
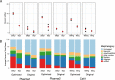
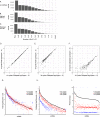
MicroRNAs hold great promise as biomarkers of disease. However, there are few efficient and robust methods for measuring microRNAs from low input samples. Here, we develop a high-throughput sequencing protocol that efficiently captures small RNAs while minimizing inherent biases associated with library production. The protocol is based on early barcoding such that all downstream manipulations can be performed on a pool of many samples thereby reducing reagent usage and workload. We show that the optimization of adapter concentrations along with the addition of nucleotide modifications and random nucleotides increases the efficiency of small RNA capture. We further show, using unique molecular identifiers, that stochastic capture of low input RNA rather than PCR amplification influences the biased quantitation of intermediately and lowly expressed microRNAs. Our improved method allows the processing of tens to hundreds of samples simultaneously while retaining high efficiency quantitation of microRNAs in low input samples from tissues or bodily fluids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Xu C, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008;18:cr2008282. - PubMed
-
- Calin, G. A., Schwarzenbach, H., Pantel, K. & Nishida, N. Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 11, nrclinonc.2014.5 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 5F31CA200163/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)/International
- U19CA179512/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)/International
- R01 CA198145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007470/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

