Analysis of expression levels of IL-17 and IL-34 and influencing factors for prognosis in patients with lupus nephritis
- PMID: 30783486
- PMCID: PMC6364195
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7168
Analysis of expression levels of IL-17 and IL-34 and influencing factors for prognosis in patients with lupus nephritis
Abstract
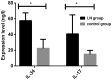
Expression levels of interleukin-17 (IL-17) and IL-34 was investigated to analyze the influencing factors for prognosis in patients with lupus nephritis (LN). Clinical data of 45 patients (LN group) treated and diagnosed with LN via renal biopsy in Yanan University Affiliated Hospital from October 2010 to October 2012 and 50 healthy subjects (control group) were analyzed retrospectively. Levels of serum IL-17 and IL-34 were detected via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Correlations of serum IL-17 and IL-34 with urinary protein in LN patients were analyzed via Pearson correlation analysis. Univariate survival analysis was performed using the Kaplan-Meier method, and multivariate analysis was performed for LN prognosis using the Cox proportional hazards model. Levels of serum IL-34 and IL-17 in patients in LN group were significantly higher than those in control group (P<0.001). Serum IL-17 and IL-34 in LN patients were positively correlated with urinary protein (r= 0.436 and 0.714, P<0.05). Adverse factors affecting the prognosis of 45 LN patients including age, hemoglobin, platelet, blood uric acid, urinary protein, IL-17 and IL-34, showing statistically significant differences (P<0.05). Age, hemoglobin, blood uric acid, urinary protein, IL-17 and IL-34 were independent risk factors for poor prognosis of LN (P<0.05). The inflammatory factors IL-17 and IL-34 are highly expressed in the serum of LN patients. Levels of serum IL-17 and IL-34 in LN patients have positive correlations with urinary protein. Results of univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses reveal that age, hemoglobin, blood uric acid, urinary protein, IL-17 and IL-34 are independent risk factors for poor prognosis of LN. IL-17 and IL-34 can therefore serve as effective indexes for clinical diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of LN.
Keywords: IL-17; IL-34; influencing factors for prognosis; lupus nephritis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum Uric Acid is Associated with Renal Prognosis of Lupus Nephritis in Women but not in Men.J Clin Med. 2020 Mar 12;9(3):773. doi: 10.3390/jcm9030773. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32178386 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation analysis of TLR9 and IL-23 expression in patients with lupus nephritis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Apr;23(7):2944-2949. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201904_17574. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31002145
-
Interleukin-32γ: Possible association with the activity and development of nephritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Int J Rheum Dis. 2019 Jul;22(7):1305-1311. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13550. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Int J Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 30941928
-
Urinary interleukin 22 binding protein as a marker of lupus nephritis in Egyptian children with juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Feb;37(2):451-458. doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3812-5. Epub 2017 Sep 9. Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 28887660
-
Interferon-Inducible Protein 10 and Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 8;20(19):4954. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194954. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31597273 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Immune podocytes in the immune microenvironment of lupus nephritis (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2023 Nov;28(5):204. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13091. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 37711069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between immunoglobulin G N-glycosylation and lupus nephritis in female patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case-control study.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 21;14:1257906. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1257906. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37809087 Free PMC article.
-
The Th17/IL-17 Axis and Kidney Diseases, With Focus on Lupus Nephritis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Sep 3;8:654912. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.654912. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34540858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diagnostic utility of IL-10, IL-17, and PCT in patients with sepsis infection.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 22;10:923457. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.923457. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35937269 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into renal damage in hyperuricemia: Focus on renal protection (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2025 Mar;31(3):59. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13424. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 39717954 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Faurschou M, Starklint H, Halberg P, Jacobsen S. Prognostic factors in lupus nephritis: Diagnostic and therapeutic delay increases the risk of terminal renal failure. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:1563–1569. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj S, Albert L, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Hallett DC, Ritchie S. Serial renal biopsy in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2000;27:2822–2826. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources