A rare case of perivascular epithelioid cell tumour metastases to the brain
- PMID: 30783531
- PMCID: PMC6365988
- DOI: 10.1177/2050313X19828539
A rare case of perivascular epithelioid cell tumour metastases to the brain
Abstract
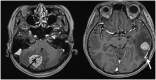
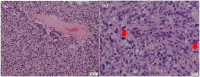
Perivascular epithelioid cell tumour is a rare mesenchymal tumour with distinct immunohistochemical profile. While it is known to occur in various anatomical sites, the central nervous system had always been a protected site for primary or secondary perivascular epithelioid cell tumours. We describe a 61-year-old lady who presented with symptoms of raised intracranial pressure, 3 months after the resection of duodenal and thoracic tumours which were histologically consistent with perivascular epithelioid cell tumour. She was investigated and then subsequently subjected to resection of two metastatic intracranial lesions. The radiological, intraoperative as well as histopathological findings of the metastatic lesions are discussed. Metastatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumour of the brain is extremely rare. However, patients who are stratified as high risk for recurrence or metastases should undergo an early magnetic resonance imaging/computed tomography of the brain in addition to a whole-body positron emission tomography scan, to allow for early detection and management of these tumours.
Keywords: Perivascular epithelioid cell tumour; brain; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Bonetti F, Pea M, Martignoni G, et al. PEC and sugar. Am J Surg Pathol 1992; 16(3): 307–308. - PubMed
-
- Parfitt JR, Keith JL, Megyesi JF, et al. Metastatic PEComa to the brain. Acta Neuropathol 2006; 112: 349. - PubMed
-
- Folpe AL. Neoplasms with perivascular epithelioid cell differentiation (PEComas). In: Fletcher CDM, Unni KK, Mertens F. (eds) Pathology & genetics: tumors of soft tissue and bone series (WHO Classification of tumors). Lyon: IARC Press, 2002, pp. 221–222.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

