Intravitreal Injection of 1.25% Povidone Iodine Followed by Vitrectomy Using 0.025% Povidone Iodine Irrigation for Treating Endophthalmitis
- PMID: 30783556
- PMCID: PMC6375116
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.8.1.21
Intravitreal Injection of 1.25% Povidone Iodine Followed by Vitrectomy Using 0.025% Povidone Iodine Irrigation for Treating Endophthalmitis
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the safety and effectiveness of intravitreal injection (IVI) of 1.25% povidone iodine (PI) followed by vitrectomy using 0.025% PI irrigation for treating endophthalmitis.
Methods: Prospective case series study. Nine eyes of 8 patients with postoperative or endogenous endophthalmitis treated at the Nihon University Hospital between April 2015 and October 2017 were studied. First, IVI of 0.1 mL/1.25%PI was conducted, followed by anterior chamber irrigation and vitrectomy using 0.025%PI irrigation solution. Corneal epithelial damage, anterior chamber inflammation, and vitreous inflammation were assessed and fundus examinations were performed, using a slit-lamp microscope and indirect ophthalmoscopy. A specular microscope, Goldmann perimetry, and electroretinography (ERG) were also used.
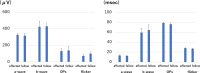
Results: In all but case 7, endophthalmitis resolved rapidly and good visual acuity was maintained. No adverse events were noted. Furthermore, the perioperative ERG showed improvements in the oscillatory potentials amplitudes on ERG and flicker ERG, as well as in the implicit time of the a-wave, suggesting functional recovery in the retinal outer and inner layers after therapy.
Conclusions: IVI of PI followed by vitrectomy was thought to be a safe and effective treatment for endophthalmitis.
Translational relevance: We succeeded in proving the clinical safety of IVI of PI followed by vitrectomy with PI irrigation as well as previous experimental reports. PI is available in world widely, therefore this method will be optimal treatment for endophthalmitis.
Keywords: electroretinogram; endophthalmitis; intravitreal injection; povidone iodine; vitrectomy.
Figures


References
-
- Ciulla TA, Starr MB, Masket S. Bacterial endophthalmitis prophylaxis for cataract surgery: an evidence-based update. Ophthalmology. 2002;109:13–24. - PubMed
-
- Carrim ZI, Mackie G, Gallacher G, Wykes WN. The efficacy of 5% povidone-iodine for 3 minutes prior to cataract surgery. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2009;19:560–564. - PubMed
-
- Rikimaru T, Kondo M, Kajimura K, et al. Efficacy of common antiseptics against multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2002;6:763–770. - PubMed
-
- Bonowitz A, Schaller M, Laude J, Reimer K, Korting HC. Comparative therapeutic and toxic effects of different povidone iodine (PVP-I) formulations in a model of oral candidosis based on in vitro reconstituted epithelium. J Drug Target. 2001;9:75–83. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

